Cinoxacin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
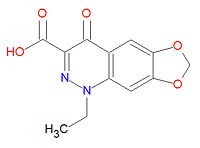
{{Image|Cinoxacin structure.jpg|right|200px|Cinoxacin}} | |||
'''Cinoxacin''' ('''Cinobac®''') is an [[antibiotic]] drug use to treat [[urinary tract infection]]s caused by many aerobic, | '''Cinoxacin''' ('''Cinobac®''') is an [[antibiotic]] drug use to treat [[urinary tract infection]]s caused by many aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria. It is active against susceptible strains of [[E. coli]], [[Proteus mirabilis]], [[Proteus vulgaris]], [[Klebsiella pneumoniae]], and [[Enterobacter]] species. | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
{{CZMed}} | {{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:02, 28 July 2024
Cinoxacin (Cinobac®) is an antibiotic drug use to treat urinary tract infections caused by many aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria. It is active against susceptible strains of E. coli, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Enterobacter species.
Mechanism of action
Cinoxacin binds to DNA and interferes with the synthesis of viral RNA and therefore inhibits the production of viral proteins.
Chemistry
Cinoxacin's IUPAC chemical name is 1-ethyl-4-oxo-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]cinnoline-3-carboxylic acid and its chemical formula is C12H10N2O5 (MW=262.2182 g/mol). It is related to oxolinic acid and nalidixic acid and it is active over the entire urinary pH range.
External links
The most up-to-date information about Cinoxacin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Cinoxacin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cinoxacin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cinoxacin - Detailed information from DrugBank.