Cefadroxil: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|width=250px | |width=250px | ||
|molname=cefadroxil | |molname=cefadroxil | ||
|synonyms=''' | |synonyms='''cefradroxil''' | ||
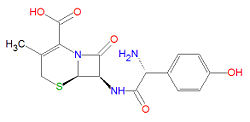
|molformula= C<sub>16</sub>H<sub>17</sub>N<sub>3</sub>O<sub>5</sub>S | |molformula= C<sub>16</sub>H<sub>17</sub>N<sub>3</sub>O<sub>5</sub>S | ||
|molmass=363.3883 | |molmass=363.3883 | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Cefadroxil''' is a first-generation [[cephalosporin]] antibiotic, is used to treat urinary tract infections, skin infections, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis. The compound is active against bacteria due to the [[beta-lactam]] moiety and thus is similar to [[penicillin]]. | '''Cefadroxil''' is a first-generation [[cephalosporin]] antibiotic, is used to treat urinary tract infections, skin infections, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis. The compound is active against bacteria due to the [[beta-lactam]] moiety and thus is similar to [[penicillin]]. Cefadroxil can be used to treat infections of [[S. pneumoniae]], [[H. influenzae]], [[staphylococci]], [[S. pyogenes]], [[E. coli]], [[P. mirabilis]], [[Klebsiella sp]], coagulase-negative staphylococci and Streptococcus pyogenes. | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
*Sumacef® | *Sumacef® | ||
*Ultracef® | *Ultracef® | ||
== External links == | |||
{{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 25 July 2024
|
| |||||||
| cefadroxil | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Cefadroxil is a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, is used to treat urinary tract infections, skin infections, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis. The compound is active against bacteria due to the beta-lactam moiety and thus is similar to penicillin. Cefadroxil can be used to treat infections of S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, staphylococci, S. pyogenes, E. coli, P. mirabilis, Klebsiella sp, coagulase-negative staphylococci and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Mechanism of action
Like all beta-lactam antibiotics, cefadroxil binds to specific penicillin-binding proteins located inside the bacterial cell wall, disrupting the last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Due to the defective bacterial cell walls, cell lysis is induced by the autolytic enzymes autolysins. Cefadroxil may interfere with an autolysin inhibitor.
Chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for cefacroxil is 7-[[2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C16H17N3O5S, giving it a molecular mass of 363.3883 g/mol. The compound is active against bacteria due to the presence of the beta-lactam moiety. Like other cephalosporins, it is similar to penicillin but contains a six-membered ring rather than the five-membered ring present in penicillins.
Synonyms and brand names
- Synonyms
- Cefadroxil Monohydrate
- Cefradroxil
- CDX
- Brand names
- Baxan®
- Bidocef®
- Cefa-Drops®
- Cefamox®
- Cephos®
- Duracef®
- Kefroxil®
- Oracefal®
- Sedral®
- Sumacef®
- Ultracef®
External links
The most up-to-date information about Cefadroxil and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Cefadroxil - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefadroxil - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefadroxil - Detailed information from DrugBank.