Animal/Gallery: Difference between revisions
< Animal
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Joshua Choi (New page: {{subpages}} {{Gallery-mixed |caption=Add an optional subheading here. |width=200 |lines=7 |Grey Nurse Shark.jpg|Smaller fish surround a grey nurse shark (''Carcharias taurus'') i...) |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Gallery-mixed | {{Gallery-mixed | ||
|caption= | |caption=The [[biodiversity]] of [[animal]]s is mind-boggling. | ||
|width= | |width=250 | ||
|lines=7 | |lines=7 | ||
|Grey Nurse Shark.jpg|Smaller [[fish]] surround a grey nurse shark ('' | |Grey Nurse Shark.jpg|Smaller [[Fish|fish]] surround a grey nurse shark (''Carcharias taurus'') in an [[Ocean|ocean]] reef cave. | ||
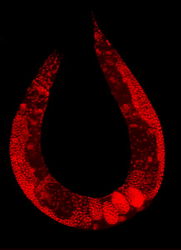
|Nematode with stained nuclei.jpg|The [[cell]]s of this [[hermaphrodite]] [[nematode]] (''[[Caenorhabditis elegans]]'') are | |Nematode with stained nuclei.jpg|The [[cell]]s of this [[Hermaphrodite|hermaphrodite]] [[Nematode|nematode]] (''[[Caenorhabditis elegans]]'') are stained so that their [[cell nucleus|nuclei]] glow red. | ||
|Ants and aphids.jpg|In one of the many unique ways animals obtain [[food]], [[rancher ant]]s drink [[sugar]]y juice from [[aphid]]s (''[[Aphis fabae]]'') in return for the aphids' protection, an example of [[symbiosis]] and [[mutualism]]. | |Ants and aphids.jpg|In one of the many unique ways animals obtain [[food]], [[rancher ant]]s drink [[sugar]]y juice from [[aphid]]s (''[[Aphis fabae]]'') in return for the aphids' protection, an example of [[symbiosis]] and [[mutualism]]. | ||
|Red beard sponge.jpg|This [[red beard sponge]] (Microciona prolifera) washed up onshore. Sponges attach to the ocean floor and passively [[filter feeding|filter feed]] on [[plankton]] that pass through them. | |||
|Granulated sea star.jpg|This granulated [[sea star]] (''[[Choriaster granulatus]]'') is just one of the many animals that populate the [[Great Barrier Reef]]. | |||
|Ant on peony.jpg|One of the many thousands of [[ant]] [[species]] crawls on a [[peony]] [[fruit]]. Ants are essential in redistributing resources and aerating the [[soil]] in every [[continent]] except [[Antarctica]]. | |||
|Mating tortoise beetles.jpg|[[Insect]]s [[reproduction|reproduce]] in countless ways. These two mating [[tortoise beetle]]s give an example of [[internal fertilization]]. | |||
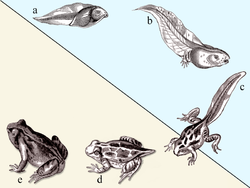
|Meyers frog metamorphosis.png|Most [[frog]]s and [[toad]]s undergo holometabolism: frog larvae, called [[tadpole]]s (or pollywogs), hatch from their [[egg]]s and change into adult frogs, which look and act differently. Tadpoles have [[gill]]s and [[fin]]s and completely live, breathe, and eat in [[water]]. Adult frogs have [[lung]]s and [[leg]]s and live, breath, and eat out of water. | |||
|Bee pollinating a wallflower.jpg|[[Bee]]s, like many [[insect]]s, [[pollination|pollinate]] [[flower]]s—transferring the flowers' [[pollen]] in return for [[nectar]], which the bees drink as [[food]]. Flowers are often [[adaptation|adapted]] to attract and accept only one species of animal. | |||
|Greek donkey with computers.jpg|Donkeys are a [[domestication|domesticated]] animal whose mechanical strength is often harnessed by humans as transportation. | |||
|Irish beach jellyfish.jpg|[[Jellyfish]] are a type of [[cnidarian]]. They are gelatinous predators that float in the [[ocean]], using [[tentacle]]s to bring whatever [[prey]] they catch into their [[mouth]]s. | |||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:13, 7 December 2022
| The biodiversity of animals is mind-boggling. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||