Nuclear power reconsidered: Difference between revisions
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (→Safety: urging reader to look at Figure 3) |
(→Cost: notes on meltdown risk, decommissioning costs) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
=== Cost === | === Cost === | ||
How will the cost compare to existing power sources including wind and solar? Existing nuclear plants have been very expensive, due to the inherent risks in pressurized water reactors (PWR's) and the need for expensive structures and burdensome regulations to deal with that risk. Newer designs promise to be much simpler, safer, and manufactured on an assembly line as replaceable parts,<ref>Elimination of "decommissioning" costs will greatly improve the long-term economy of nuclear plants [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eoU3U7TYNLA Can Nuclear Plants be Immortal, Mark Nelson]</ref> | How will the cost compare to existing power sources including wind and solar? Existing nuclear plants have been very expensive, due to the inherent risks in solid-fuel pressurized water reactors (PWR's) and the need for expensive structures and burdensome regulations to deal with that risk. Newer designs promise to be much simpler, safer, and manufactured on an assembly line as replaceable parts, rather than site built. Elimination of water at high pressure and temperature avoids the risk of steam explosions. Reactor vessels with non-destructive "meltdown" behavior avoid the risk of another Fukushima.<ref>A liquid fuel reactor can have plugs at the bottom of the reactor vessel that melt if the reactor gets too hot. The fuel then flows safely into drain tanks.</ref> | ||
Plants with replaceable parts can operate indefinitely,<ref>Elimination of "decommissioning" costs will greatly improve the long-term economy of nuclear plants [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eoU3U7TYNLA Can Nuclear Plants be Immortal, Mark Nelson]</ref> but if a plant is decommissioned, the process is little more than pulling out but not replacing all the parts. Cost is a lesser worry than the other issues, because the risk can be born by private companies promising to deliver reactors at an agreed price.<ref>ThorCon has presented a [https://thorconpower.com/economics detailed analysis] showing the cost of their proposed plants as less than a coal plant.</ref> See [[Cost_of_nuclear_power]] for further discussion. | |||
One remaining worry is future costs if fuel or some essential material becomes scarce. Some PWR's require hafnium in their control rods, and there was worry about the world supply of hafnium if thousands of these reactors were to be deployed in the coming decades.<ref>D. Abbott, "Is Nuclear Power Globally Scalable?" Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 99, no. 10, pp. 1611-1617, Oct. 2011, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6021978. See section XIII on the hafnium problem.</ref> | One remaining worry is future costs if fuel or some essential material becomes scarce. Some PWR's require hafnium in their control rods, and there was worry about the world supply of hafnium if thousands of these reactors were to be deployed in the coming decades.<ref>D. Abbott, "Is Nuclear Power Globally Scalable?" Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 99, no. 10, pp. 1611-1617, Oct. 2011, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6021978. See section XIII on the hafnium problem.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:50, 13 November 2022
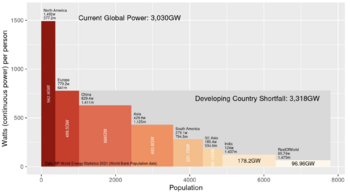
Fig.1 Electricity consumption may soon double, mostly from coal-fired power plants in the developing world.[1]
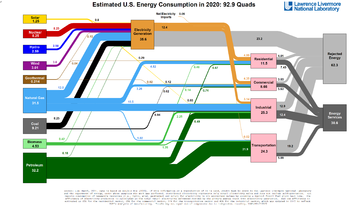
Decades of failure to slow the rising global consumption of coal, oil and gas[4] has led to a reconsideration of nuclear power using innovative reactor designs. Nuclear power generators can provide affordable, reliable, dispatchable[5] electricity to the grid regardless of weather. While nuclear fuel is not renewable, nuclear power generation produces little air pollution as compared with highly polluting fossil fuels such as coal, oil or gas.
Demand for electricity is high and still increasing, and wind and solar generators, while useful, will not be able to meet the demand in many locations. Fossil fuels are in increasingly short supply, are costly to mine and transport, and they pollute the air badly. Meeting the world's needs for reliable carbon-free electricity generation could require thousands of nuclear plants, or perhaps a breakthrough in technology to store energy from wind and solar.[6][7][8] See Figs. 1 and 2 on the magnitude of the world energy challenge.
Issues that have held back widespread use of nuclear power include safety, waste management, cost, and concerns about nuclear materials falling into the hands of bad actors. Several new reactor designs have been proposed that seek to address these issues.
It is important that all arguments for and against these new reactor designs be published for public comment. Scrutiny from people who have engineering experience, but are not connected to the nuclear industry or any political advocacy group, are particularly useful.
Issues Confronting the Nuclear Industry
Safety
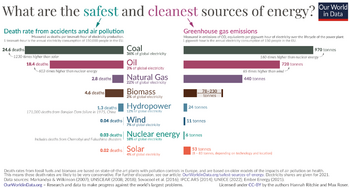
Nuclear accidents have been compared to airplane crashes - in the public mind, they seem to loom far more horrible than the situation actually warrants. Figure 3 shows how many more casualties worldwide are resulting from the use of fossil fuels and other energy sources. Widespread deployment of nuclear reactors would require the new designs to address not only the fears [10] that have arisen from accidents in the past, but also what might be conceivable in the future, including natural disasters and sabotage. Nuclear power over the last 50 years, when measured by objective criteria like number of deaths per terawatt hour of energy produced, has been safer than even natural gas (the safest of the fossil fuels), and comparable to wind and solar (Fig.3). The new designs will be even safer.
Because even a nearly harmless malfunction can influence public opinion strongly enough to set back deployment of nuclear power for decades, some of the new designs are "walk away safe" - that is, they are designed with the ability to shut down safely even if the operators just walk away and do nothing to prevent an accident. This article calls this level of safety S-1.
Beyond that, operators could require safety level S-2 - that is, no way the operators (or terrorists) can cause a radiation leak by overriding the normal controls.
Finally, operators could require safety level S-3, the highest level of safety - that is, no way, even using explosives, that terrorists could cause a leak. S-3 may be impossible to achieve. In that case, we must consider possible scenarios and what the operator response would need to be.
Scenario Sab-1: Terrorists arrive with cable cutters, a hacksaw, and a memory stick with some malware from North Korea.[11] The operators are expelled, except one, whose daughter is held hostage, and will be killed if anything goes wrong with the terrorist plan.
Scenario Sab-2: The terrorists have heavy equipment to drill through concrete, and a pump truck with some kind of explosive liquid.
Scenario Sab-3: The terrorists have hired El Chapo's tunneling team to come at the reactor from underground.
There may be dozens of scenarios to consider, including tsunamis, hijacked airplanes, and even a meteorite strike. The public should be encouraged, perhaps even rewarded for submitting scenarios worthy of consideration. The Fukushima disaster could have been avoided, if someone had thought to keep pump trucks on a nearby hill.
Waste Management
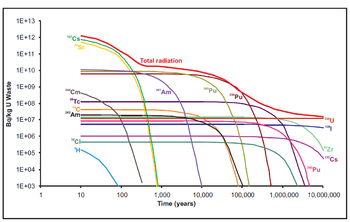
How much waste is produced compared to other sources of energy? How will it be contained, and what are the dangers to people and the environment? Like questions on safety, public perception of the dangers of nuclear waste is much worse than historical data shows.[13] The volume of waste per per terawatt-hour is 100,000 times less than coal.[14] Even if we look only at radioactivity released to the environment,[15] watt-for-watt nuclear power is 100 times less than coal.[16]
Much of the worry about nuclear waste centers around the long life of some isotopes in the waste (See Fig.4). There is concern about leakage into the environment decades or even centuries from now. Billion-dollar efforts to bury the waste deep under a mountain have only heightened public fears. Dry-cask storage at the power plants has proven to be a safe but temporary solution.[17] This interim storage has the advantage of being able to recover the "waste" and use it in newer reactors that can use the remaining 95% of available energy.
Transportation of spent fuel from reactors to disposal or reprocessing sites must be done safely. Reprocessing should be done at secure locations to avoid diversion of dangerous materials.[18] Leakage into groundwater and ocean water near shore is a special concern. New reactor designs must address these concerns, even though they go beyond the design of the reactor itself. Will the waste be solid or liquid? Will it require special casks, or even special vehicles for transportation on public roads? (See Fig.5)
Other worries include the possibility of sabotage or theft of waste material that might be useful in a "dirty bomb". Again, we should evaluate specific plans by considering likely scenarios. Is the storage facility away from any population center and not a target for an airplane crash, a truck bomb, or even a short-range missile? Is there a secure perimeter with intrusion detectors? If there is an intrusion, is cutting through the concrete and steel difficult enough that there will be plenty of time for a response from local law enforcement, or even a nearby military base? (See Fig.6)
It is important that we make a distinction between spent fuel from nuclear power, and the waste from bomb production, which was often done in a rush with little concern for pollution. Spent fuel rods can be stored safely. Weapons waste poses a much bigger problem due to the large variety and sometimes unexpected characteristics of the material to be buried.[20] In evaluating a new reactor design, we must look at the complete fuel cycle, not just the waste from the reactor itself. Are there any problems with the mining, processing, or transportation of the fuel, or with the reprocessing of spent fuel?
See Nuclear_waste_management for further discussion.
Weapons Proliferation
Will deployment of reactors to untrusted countries, or countries that might be taken over by rogue actors, increase the risk of proliferation, either by theft of materials in the reactor, or by modification of the reactor to produce weapons-grade materials? Will fuel processing or other activities connected with nuclear power provide cover for a weapons program? Will knowledge of the new reactor designs lead to easier ways to make bombs?
There are three nuclides with potential for making a bomb: U-233, U-235, and Pu-239. Every reactor design has a characteristic isotopic composition in its fuel, which evolves over time as the fuel is consumed. Some uranium reactors have a brief period in their fuel cycle where weapons-grade Pu-239 can be extracted from the partially used fuel. Some thorium reactors with on-site fuel processing may be vulnerable to skimming of a small fraction of U-233 from the process loop.[21] Some molten salt reactors start with uranium enriched to 20% U-235, and that might provide a head-start to a country wanting to enrich all the way to bomb-grade.
Considerations like these favor designs in which all fuel processing is done at secure locations, and there is never any weapons grade material easily extracted from an operating reactor. The requirement should not be perfection, but simply that a new reactor should not allow an easier route to bomb making than currently available centrifuges.
Cost
How will the cost compare to existing power sources including wind and solar? Existing nuclear plants have been very expensive, due to the inherent risks in solid-fuel pressurized water reactors (PWR's) and the need for expensive structures and burdensome regulations to deal with that risk. Newer designs promise to be much simpler, safer, and manufactured on an assembly line as replaceable parts, rather than site built. Elimination of water at high pressure and temperature avoids the risk of steam explosions. Reactor vessels with non-destructive "meltdown" behavior avoid the risk of another Fukushima.[22]
Plants with replaceable parts can operate indefinitely,[23] but if a plant is decommissioned, the process is little more than pulling out but not replacing all the parts. Cost is a lesser worry than the other issues, because the risk can be born by private companies promising to deliver reactors at an agreed price.[24] See Cost_of_nuclear_power for further discussion.
One remaining worry is future costs if fuel or some essential material becomes scarce. Some PWR's require hafnium in their control rods, and there was worry about the world supply of hafnium if thousands of these reactors were to be deployed in the coming decades.[25] As for the supply of fuel, the World Nuclear Association says it is essentially unlimited.[26] Some of the new reactors can burn[27] all the uranium, not just the 0.7% now burned by PWRs, and they can even burn thorium, which is three times more abundant than uranium.
Proposed Designs
Here is a brief summary of several promising designs. Click on the heading for a response to the issues raised in this article.
MSR
This is a Molten Salt Reactor based on proven technology, intended for a short-term solution (decades) while more advanced designs are perfected.[28]
FNR
This is a Fast Neutron Reactor capable of burning spent nuclear fuel, old bomb cores, depleted uranium, and thorium.[29]
HTGR
The High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor uses helium gas as a coolant and can provide process heat for production of zero-carbon hydrogen from water.[30]
PWR
This is a smaller version of a standard Pressurized Water Reactor with all the latest safety features. [31]
Further Reading
Electrifying Our World Robert Hargraves excellent overview of energy, the growth human civilization, and possible solutions to the current climate crisis.
World Nuclear Information Library a well-organized authoritative collection of information on nuclear power.
Our World in Data has a section on Energy and Environment with nice interactive graphics.
Notes and References
- ↑ Fig.1.3 in Devanney "Why Nuclear Power has been a Flop". Retrieved on 2022-09-17.
- ↑ "Heat from electricity is very inefficient. Using nuclear heat directly from a reactor is possible for many industrial processes.".
- ↑ "Generation of hydrogen for fuel is possible with a Very High Temperature Reactor.".
- ↑ Our World In Data. ourworldindata.org/grapher/global-primary-energy Global Energy Growth, 2022-09-17. Retrieved on 2022-09-17.
- ↑ ""Load following" is the term used by utilities, and is especially important when there is a lot of wind and solar on the grid. Some reactors are not able to do this".
- ↑ "Pumped storage is currently the most economical way to store electric power, but it requires a large reservoir on a nearby hill, or in an abandoned mine. Li-ion battery systems at $500 per KWh are not practical for utility-scale storage. See Energy Storage for a good summary of other alternatives.".
- ↑ "Utilities that include wind and solar power in their grid must have non-intermittent generating capacity (typically fossil fuels) to handle maximum demand for several days. They can save on fuel, but the cost of the plant is the same, with or without the intermittent sources.".
- ↑ "Mark Jacobson believes that long-distance transmission lines can provide an alternative to costly storage. See the bibliography for more on this proposal and the critique by Christopher Clack.".
- ↑ Our World in Data - What are the safest and cleanest sources of energy?.
- ↑ See Fear_of_radiation for discussion of these fears and the evidence contradicting widely-held beliefs about the dangers of nuclear power.
- ↑ Cybersecurity is an increasing risk for control systems connected to the Internet. See The threats from cyberspace
- ↑ https://blogs.egu.eu/network/geosphere/2015/02/02/geopoll-what-should-we-do-with-radioactive-waste/
- ↑ “Over the last 40 years, thousands of shipments of commercially generated spent nuclear fuel have been made throughout the United States without causing any radiological releases to the environment or harm to the public.” - statement by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission quoted in Storage and Disposal of Radioactive Waste
- ↑ section 2.2 "A Beautifully Small Problem" in the book Why Nuclear Power has been a Flop.
- ↑ Radioactive Wastes From Coal-fired Power Plants US Environmental Protection Agency
- ↑ https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/coal-ash-is-more-radioactive-than-nuclear-waste/ - The title is a bit misleading. From the article: "In fact, the fly ash emitted by a power plant—a by-product from burning coal for electricity—carries into the surrounding environment 100 times more radiation than a nuclear power plant producing the same amount of energy." "ounce for ounce, coal ash released from a power plant delivers more radiation than nuclear waste shielded via water or dry cask storage."
- ↑ Connecticut Yankee, a 619 MWe reactor on the Connecticut River, ran for 28 years between 1968 and 1996. The spent fuel from those 28 years is stored in 43 casks on a concrete pad, 70 feet by 228 feet.
- ↑ See Processing of Used Nuclear Fuel for discussion of various reprocessing methods and their ability to separate fissile materials from the waste.
- ↑ Transport of Radioactive Materials World Nuclear Association
- ↑ A barrel containing plutonium mixed with kitty litter exploded days after it was "safely" stored at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, leading to "Nuclear accident in New Mexico ranks among the costliest in U.S. history" LA Times
- ↑ Thorium fuel has risks, Ashley 2012, https://www.nature.com/articles/492031a
- ↑ A liquid fuel reactor can have plugs at the bottom of the reactor vessel that melt if the reactor gets too hot. The fuel then flows safely into drain tanks.
- ↑ Elimination of "decommissioning" costs will greatly improve the long-term economy of nuclear plants Can Nuclear Plants be Immortal, Mark Nelson
- ↑ ThorCon has presented a detailed analysis showing the cost of their proposed plants as less than a coal plant.
- ↑ D. Abbott, "Is Nuclear Power Globally Scalable?" Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 99, no. 10, pp. 1611-1617, Oct. 2011, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6021978. See section XIII on the hafnium problem.
- ↑ Supply of Uranium World Nuclear Association. See also Abbott 2011 for a counter-argument to the WNA assessment.
- ↑ The fissioning of nuclear fuel, sometimes called "burning" should not be confused with ordinary chemical reactions like oxidation that occurs when fossil fuels are burned.
- ↑ https://thorconpower.com/docs/docs_v130_isle20190315.pdf
- ↑ Ed Pheil, Chief Technology Officer at Elysium Industries, speaks at Thorium Energy Alliance 2020, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_ou_xswB2b0
- ↑ High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor
- ↑ https://www.science.org/news/2019/02/smaller-safer-cheaper-one-company-aims-reinvent-nuclear-reactor-and-save-warming-planet
| Authors [about]:
join in to develop this article! |