Refrigerator car: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert A. Estremo (New article generated using Special:MetadataForm) |
imported>Robert A. Estremo (start article) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
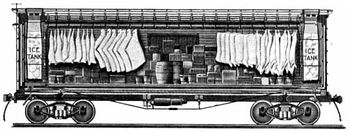
[[Image:Early refrigerator car design circa 1870.jpg||thumb|right|350px|{{Early refrigerator car design circa 1870.jpg/credit}}<br />An early refrigerator car design, ''circa'' 1870. Hatches in the roof provided access to the ice tanks at each end of the car.]] | |||
A '''refrigerator car''' (or '''"reefer"''') is a refrigerated [[boxcar]], a piece of railroad rolling stock designed to carry perishable freight at specific temperatures. Refrigerator cars differ from simple insulated boxcars and ventilated boxcars (commonly used for transporting fruit), neither of which are fitted with cooling apparatus. Reefers can be ice-cooled, come equipped with any one of a variety of mechanical refrigeration systems, or utilize carbon dioxide (either as dry ice, or in liquid form) as a cooling agent. Milk cars (and other types of "express" reefers) may or may not include a cooling system, but are equipped with high-speed wheelsets and other modifications that allow them to travel with passenger trains. Reefer applications can be divided into four broad groups: 1) dairy and poultry producers require refrigeration and special interior racks; 2) fruit and vegetable reefers tend to see seasonal use, and are generally used for long-distance shipping (for some shipments, only ventilation is necessary to remove the heat in transit created by the ripening process); 3) manufactured foods (such as canned goods and candy) as well as beer and wine do not require refrigeration, but do need the protection of an insulated car; and 4) meat reefers come equipped with specialized beef rails for handling sides of meat, and brine-tank refrigeration to provide lower temperatures (most of these units are either owned or leased by meat packing firms). | |||
Outside of North America, railroad cars which have been outfitted with cooling equipment (and designated as Class "I" by the International Union of Railways [UIC]) are generally referred to as "refrigerated vans." | |||
==History== | |||
[[Image:Illinois Central Railroad 14713.jpg|thumb|right|300px|{{Illinois Central Railroad 14713.jpg/credit}}<br />Illinois Central Railroad #14713, a ventilated fruit car dating from 1893.]] | |||
===Background=== | |||
After the end of the [[American Civil War]], [[Chicago, Illinois]] emerged as a major [[railway]] center for the distribution of livestock raised on the [[Great Plains]] to Eastern markets.<ref>Boyle and Estrada</ref> Getting the animals to market required herds to be driven up to 1,200 miles (2,000 kilometers) to railheads in [[Kansas City, Missouri]] where they were loaded into specialized [[Stock car (rail)|stock car]]s and transported live ("on-the-hoof") to regional processing centers. Driving cattle across the plains also led to tremendous weight loss, and some animals were lost along the way. Upon arrival at the local processing facility, livestock were either slaughtered by wholesalers and delivered fresh to nearby butcher shops for retail sale, smoked, or packed for shipment in barrels of salt. Costly inefficiencies were inherent in transporting live animals by rail, particularly the fact that about sixty percent of the animal's mass is inedible. The death of animals weakened by the long drive further increased the per-unit shipping cost. Meat packer [[Gustavus Franklin Swift|Gustavus Swift]] began looking for a way to ship dressed meats from his packing plant in Chicago to the East. | |||
===Early attempts at refrigerated transport=== | |||
A number of attempts were made during the mid-1800s to ship agricultural products via rail car. As early as 1842, the [[Western Railroad of Massachusetts]] was reported in the June 15 edition of the ''Boston Traveler'' to be experimenting with innovative [[freight car]] designs capable of carrying all types of perishable goods without spoilage.<ref>White, p. 31</ref> The first refrigerated boxcar entered service in June 1851, on the [[Northern Railroad of New York]] (or NRNY, which later became part of the [[Rutland Railroad]]). This "icebox on wheels" was a limited success in that it was only able to function in cold weather. That same year, the [[Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad]] (O&LC) began shipping butter to Boston in purpose-built freight cars, utilizing ice to cool the contents. The first consignment of dressed beef left the Chicago stockyards in 1857 in ordinary [[boxcar]]s retrofitted with bins filled with ice. Placing meat directly against ice resulted in discoloration and affected the taste, and proved impractical. During the same period Swift experimented by moving cut meat using a string of ten boxcars which ran with their doors removed, and made a few test shipments to [[New York]] during the winter months over the [[Grand Trunk Railway]] (GTR). The method proved too limited to be practical. | |||
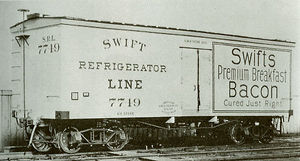
[[Image:Swift Refrigerator Line car circa 1899.jpg|thumb|right|300px|{{Swift Refrigerator Line car circa 1899.jpg/credit}}<br />A builder's photo of one of the first refrigerator cars to come out of the Detroit plant of the American Car and Foundry Company (ACF), built in 1899 for the Swift Refrigerator Line.]] | |||
[[Detroit, Michigan|Detroit's]] William Davis patented a refrigerator car that employed metal racks to suspend the carcasses above a frozen mixture of ice and salt. He sold the design in 1868 to industrialist George H. Hammond, a Detroit meat packer, who built a set of cars to transport his products to Boston using ice from the [[Great Lakes]] for cooling.<ref>White, p. 33</ref> The load had the tendency of swinging to one side when the car entered a curve at high speed, and the use of the units was discontinued after several derailments. In 1878 Swift hired engineer Andrew Chase to design a ventilated car that was well insulated, and positioned the ice in a compartment at the top of the car, allowing the chilled air to flow naturally downward.<ref>White, p. 45</ref> The meat was packed tightly at the bottom of the car to keep the [[center of gravity]] low and to prevent the cargo from shifting. Chase's design proved to be a practical solution to providing temperature-controlled carriage of dressed meats, and allowed Swift and Company to ship their products all over the [[United States]] and internationally. Swift's attempts to sell Chase's design to major railroads were rebuffed, as the companies feared that they would jeopardize their considerable investments in stock cars, animal pens, and feedlots if refrigerated meat transport gained wide acceptance. In response, Swift financed the initial production run on his own, then — when the American roads refused his business — he contracted with the GTR (a railroad that derived little income from transporting live cattle) to haul the cars into [[Michigan]] and then eastward through [[Canada]]. In 1880 the [[Peninsular Car Company]] (subsequently purchased by ACF) delivered the first of these units to Swift, and the Swift Refrigerator Line (SRL) was created. Within a year the Line’s roster had risen to nearly 200 units, and Swift was transporting an average of 3,000 carcasses a week to [[Boston, Massachusetts]]. Competing firms such as [[Armour and Company]] quickly followed suit. By 1920 the SRL owned and operated 7,000 of the ice-cooled rail cars. The [[General American Transportation Corporation]] assumed ownership of the line in 1930. | |||
[[Image:Tiffany ad 1879 CBD.jpg|thumb|right|300px|{{Tiffany ad 1879 CBD.jpg/credit}}<br />An advertisement taken from the 1st edition (1879) of the Car-Builders Dictionary for the Tiffany Refrigerator Car Company, a pioneer in the design of refrigerated railroad cars.]] | |||
'''Live cattle and dressed beef deliveries to New York ([[short tons]]):''' <ref>''Railway Review'', January 29, 1887, p. 62: The subject cars travelled on the [[Erie Railroad|Erie]], [[Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad|Lackawanna]], [[New York Central Railroad|New York Central]], and [[Pennsylvania Railroad|Pennsylvania]] railroads.</ref> | |||
{| class="toccolours" | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
|align=center | <small>''(Stock Cars)'' | |||
|align=center | <small>''(Refrigerator Cars)'' | |||
|- | |||
|align=center | '''Year | |||
|align=center | '''Live Cattle | |||
|align=center | '''Dressed Beef | |||
|- | |||
| 1882 | |||
|align=center | 366,487 | |||
|align=center | 2,633 | |||
|- | |||
| 1883 | |||
|align=center | 392,095 | |||
|align=center | 16,365 | |||
|- | |||
| 1884 | |||
|align=center | 328,220 | |||
|align=center | 34,956 | |||
|- | |||
| 1885 | |||
|align=center | 337,820 | |||
|align=center | 53,344 | |||
|- | |||
| 1886 | |||
|align=center | 280,184 | |||
|align=center | 69,769 | |||
|} | |||
'''19th Century American Refrigerator Cars:''' <ref>Source: ''Poor's Manual of Railroads'' and [[Interstate Commerce Commission|ICC]] and [[U.S. Census]] reports.</ref> | |||
{| class="toccolours" | |||
|- | |||
|align=center | '''Year | |||
|align=center | '''Private Lines | |||
|align=center | '''Railroads | |||
|align=center | '''Total | |||
|- | |||
| 1880 | |||
|align=center | 1,000 ''est. | |||
|align=center | 310 | |||
|align=center | 1,310 ''est. | |||
|- | |||
| 1885 | |||
|align=center | 5,010 ''est. | |||
|align=center | 990 | |||
|align=center | 6,000 ''est. | |||
|- | |||
| 1890 | |||
|align=center | 15,000 ''est. | |||
|align=center | 8,570 | |||
|align=center | 23,570 ''est. | |||
|- | |||
| 1895 | |||
|align=center | 21,000 ''est | |||
|align=center | 7,040 | |||
|align=center | 28,040 ''est. | |||
|- | |||
| 1900 | |||
|align=center | 54,000 ''est. | |||
|align=center | 14,500 | |||
|align=center | 68,500 ''est. | |||
|} | |||
===The "Ice Age"=== | |||
[[Image:Ice Harvesting on Lake St Clair Michigan circa 1905.jpg|thumb|right|300px|{{Ice Harvesting on Lake St Clair Michigan circa 1905.jpg/credit}}<br />Men harvest ice on Michigan's Lake Saint Clair, ''circa'' 1905. The ice would be cut into blocks and hauled by wagon to a cold storage warehouse, and held until needed.]] | |||
The use of ice to refrigerate and thus preserve food dates back to prehistoric times. Through the ages, the seasonal harvesting of snow and ice was a regular practice of many cultures. [[China]], [[Greece]], and [[Rome]] (to name a few) all stored ice and snow in caves or dugouts lined with straw or other insulating materials. Rationing of the ice allowed the preservation of foods during hot periods, a practice that was successfully employed for centuries. For most of the 1800s, natural ice (harvested from ponds and lakes) was used to supply refrigerator cars. At high altitudes or northern latitudes, one foot tanks were often filled with water and allowed to freeze. Ice was typically cut into blocks during the winter and stored in insulated warehouses for later use, with sawdust and hay packed around the ice blocks to provide additional insulation. A late-19th century wood-bodied reefer required reicing every 250 to 400 miles. By the turn of the 20th Century manufactured ice became more common. The Pacific Fruit Express (PFE), for example, maintained 7 natural harvesting facilities, and operated 18 artificial ice plants. Their largest plant (located in [[Roseville, California]]) produced 1,200 "short" tons of ice daily, and Roseville’s docks could accommodate up to 254 cars. At the industry’s peak, 13 million short tons of ice was produced for refrigerator car use annually. | |||
===="Top Icing"==== | |||
Top icing is the practice of placing a 2- to 4-inch layer of crushed ice over the top of agricultural products that have high respiration rates, need high relative humidity, and benefit from having the cooling agent sit directly atop the load (or within individual boxes). Cars with pre-cooled fresh produce were top iced just before shipment. Top icing added considerable dead weight to the load. Top-icing a 40-foot reefer required in over 10,000 pounds of ice. It had been postulated that as the ice melts, the resulting chilled water would trickle down through the load to continue the cooling process. It was found, however, that top-icing only benefited the uppermost layers of the cargo, and that the water from the melting ice often passed through spaces between the cartons and pallets with little or no cooling effect. It was ultimately determined that top-icing is useful only in preventing an increase in temperature, and was eventually discontinued. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Top icing reefer.jpg|{{Top icing reefer.jpg/credit}}<br />Top icing a reefer. | |||
Image:Topping off FGE reefer with ice.jpg|{{Topping off FGE reefer with ice.jpg/credit}}<br />Workmen fill up an FGE reefer's top-mounted bunkers with crushed ice. | |||
Image:Men loading ice blocks into reefers.jpg|{{Men loading ice blocks into reefers.jpg/credit}}<br />Ice blocks (also called "cakes") are manually placed into reefers from a covered icing dock.<ref>Each block weighed between 200 and 400 pounds; crushed ice was typically used for meat cars.</ref> | |||
Image:Mechanical ice loader.jpg|{{Mechanical ice loader.jpg/credit}}<br />The "business end" of a mechanical ice loading system services a line of Pacific Fruit Express refrigerator cars.<ref>Each car will require approximately 5½ "short" tons (5 metric tons) of ice.</ref> | |||
</gallery> | |||
The typical service cycle for an ice-cooled produce reefer (generally handled as a part of a block of cars): | |||
# The cars were cleaned with hot water or steam. | |||
# Depending on the cargo, the cars might have undergone 4 hours of "pre-cooling" prior to loading, which entailed blowing in cold air through one ice hatch and allowing the warmer air to be expelled through the other hatches. The practice, dating back almost to the inception of the refrigerator car, saved ice and resulted in fresher cargo. | |||
# The cars' ice bunkers were filled, either manually from an [http://www.uprr.com/aboutup/photos/pfe/graphics/24.jpg icing dock], via mechanical loading equipment, or (in locations where demand for ice was sporadic) using specially-designed [http://www.uprr.com/aboutup/photos/pfe/graphics/spe11-71.jpg field icing cars]. | |||
# The cars were delivered to the shipper for loading, and the ice was topped-off. | |||
# Depending on the cargo and destination, the cars may have been fumigated. | |||
# The train would depart for the eastern markets. | |||
# The cars were reiced in transit approximately once a day. | |||
# Upon reaching their destination, the cars were unloaded. | |||
# If in demand, the cars would be returned to their point of origin empty. If not in demand, the cars would be cleaned and (if possible) used for a dry shipment. | |||
Refrigerator cars required effective insulation to protect their contents from temperature extremes. "Hairfelt" derived from compressed cattle hair, sandwiched into the floor and walls of the car, was inexpensive but flawed — over its three- to four-year service life it would decay, rotting out the car's wooden partitions and tainting the cargo with a foul odor. The higher cost of other materials such as "Linofelt" (woven from flax fibers) or cork prevented their widespread adoption. Synthetic materials such as [[fiberglass]] and [[polystyrene]], both introduced after [[World War II]], offered the most cost-effective and practical solution. | |||
==Notes and references== | |||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
Revision as of 13:56, 14 August 2013
A refrigerator car (or "reefer") is a refrigerated boxcar, a piece of railroad rolling stock designed to carry perishable freight at specific temperatures. Refrigerator cars differ from simple insulated boxcars and ventilated boxcars (commonly used for transporting fruit), neither of which are fitted with cooling apparatus. Reefers can be ice-cooled, come equipped with any one of a variety of mechanical refrigeration systems, or utilize carbon dioxide (either as dry ice, or in liquid form) as a cooling agent. Milk cars (and other types of "express" reefers) may or may not include a cooling system, but are equipped with high-speed wheelsets and other modifications that allow them to travel with passenger trains. Reefer applications can be divided into four broad groups: 1) dairy and poultry producers require refrigeration and special interior racks; 2) fruit and vegetable reefers tend to see seasonal use, and are generally used for long-distance shipping (for some shipments, only ventilation is necessary to remove the heat in transit created by the ripening process); 3) manufactured foods (such as canned goods and candy) as well as beer and wine do not require refrigeration, but do need the protection of an insulated car; and 4) meat reefers come equipped with specialized beef rails for handling sides of meat, and brine-tank refrigeration to provide lower temperatures (most of these units are either owned or leased by meat packing firms).
Outside of North America, railroad cars which have been outfitted with cooling equipment (and designated as Class "I" by the International Union of Railways [UIC]) are generally referred to as "refrigerated vans."
History
Background
After the end of the American Civil War, Chicago, Illinois emerged as a major railway center for the distribution of livestock raised on the Great Plains to Eastern markets.[1] Getting the animals to market required herds to be driven up to 1,200 miles (2,000 kilometers) to railheads in Kansas City, Missouri where they were loaded into specialized stock cars and transported live ("on-the-hoof") to regional processing centers. Driving cattle across the plains also led to tremendous weight loss, and some animals were lost along the way. Upon arrival at the local processing facility, livestock were either slaughtered by wholesalers and delivered fresh to nearby butcher shops for retail sale, smoked, or packed for shipment in barrels of salt. Costly inefficiencies were inherent in transporting live animals by rail, particularly the fact that about sixty percent of the animal's mass is inedible. The death of animals weakened by the long drive further increased the per-unit shipping cost. Meat packer Gustavus Swift began looking for a way to ship dressed meats from his packing plant in Chicago to the East.
Early attempts at refrigerated transport
A number of attempts were made during the mid-1800s to ship agricultural products via rail car. As early as 1842, the Western Railroad of Massachusetts was reported in the June 15 edition of the Boston Traveler to be experimenting with innovative freight car designs capable of carrying all types of perishable goods without spoilage.[2] The first refrigerated boxcar entered service in June 1851, on the Northern Railroad of New York (or NRNY, which later became part of the Rutland Railroad). This "icebox on wheels" was a limited success in that it was only able to function in cold weather. That same year, the Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad (O&LC) began shipping butter to Boston in purpose-built freight cars, utilizing ice to cool the contents. The first consignment of dressed beef left the Chicago stockyards in 1857 in ordinary boxcars retrofitted with bins filled with ice. Placing meat directly against ice resulted in discoloration and affected the taste, and proved impractical. During the same period Swift experimented by moving cut meat using a string of ten boxcars which ran with their doors removed, and made a few test shipments to New York during the winter months over the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR). The method proved too limited to be practical.
Detroit's William Davis patented a refrigerator car that employed metal racks to suspend the carcasses above a frozen mixture of ice and salt. He sold the design in 1868 to industrialist George H. Hammond, a Detroit meat packer, who built a set of cars to transport his products to Boston using ice from the Great Lakes for cooling.[3] The load had the tendency of swinging to one side when the car entered a curve at high speed, and the use of the units was discontinued after several derailments. In 1878 Swift hired engineer Andrew Chase to design a ventilated car that was well insulated, and positioned the ice in a compartment at the top of the car, allowing the chilled air to flow naturally downward.[4] The meat was packed tightly at the bottom of the car to keep the center of gravity low and to prevent the cargo from shifting. Chase's design proved to be a practical solution to providing temperature-controlled carriage of dressed meats, and allowed Swift and Company to ship their products all over the United States and internationally. Swift's attempts to sell Chase's design to major railroads were rebuffed, as the companies feared that they would jeopardize their considerable investments in stock cars, animal pens, and feedlots if refrigerated meat transport gained wide acceptance. In response, Swift financed the initial production run on his own, then — when the American roads refused his business — he contracted with the GTR (a railroad that derived little income from transporting live cattle) to haul the cars into Michigan and then eastward through Canada. In 1880 the Peninsular Car Company (subsequently purchased by ACF) delivered the first of these units to Swift, and the Swift Refrigerator Line (SRL) was created. Within a year the Line’s roster had risen to nearly 200 units, and Swift was transporting an average of 3,000 carcasses a week to Boston, Massachusetts. Competing firms such as Armour and Company quickly followed suit. By 1920 the SRL owned and operated 7,000 of the ice-cooled rail cars. The General American Transportation Corporation assumed ownership of the line in 1930.
Live cattle and dressed beef deliveries to New York (short tons): [5]
| (Stock Cars) | (Refrigerator Cars) | |
| Year | Live Cattle | Dressed Beef |
| 1882 | 366,487 | 2,633 |
| 1883 | 392,095 | 16,365 |
| 1884 | 328,220 | 34,956 |
| 1885 | 337,820 | 53,344 |
| 1886 | 280,184 | 69,769 |
19th Century American Refrigerator Cars: [6]
| Year | Private Lines | Railroads | Total |
| 1880 | 1,000 est. | 310 | 1,310 est. |
| 1885 | 5,010 est. | 990 | 6,000 est. |
| 1890 | 15,000 est. | 8,570 | 23,570 est. |
| 1895 | 21,000 est | 7,040 | 28,040 est. |
| 1900 | 54,000 est. | 14,500 | 68,500 est. |
The "Ice Age"
The use of ice to refrigerate and thus preserve food dates back to prehistoric times. Through the ages, the seasonal harvesting of snow and ice was a regular practice of many cultures. China, Greece, and Rome (to name a few) all stored ice and snow in caves or dugouts lined with straw or other insulating materials. Rationing of the ice allowed the preservation of foods during hot periods, a practice that was successfully employed for centuries. For most of the 1800s, natural ice (harvested from ponds and lakes) was used to supply refrigerator cars. At high altitudes or northern latitudes, one foot tanks were often filled with water and allowed to freeze. Ice was typically cut into blocks during the winter and stored in insulated warehouses for later use, with sawdust and hay packed around the ice blocks to provide additional insulation. A late-19th century wood-bodied reefer required reicing every 250 to 400 miles. By the turn of the 20th Century manufactured ice became more common. The Pacific Fruit Express (PFE), for example, maintained 7 natural harvesting facilities, and operated 18 artificial ice plants. Their largest plant (located in Roseville, California) produced 1,200 "short" tons of ice daily, and Roseville’s docks could accommodate up to 254 cars. At the industry’s peak, 13 million short tons of ice was produced for refrigerator car use annually.
"Top Icing"
Top icing is the practice of placing a 2- to 4-inch layer of crushed ice over the top of agricultural products that have high respiration rates, need high relative humidity, and benefit from having the cooling agent sit directly atop the load (or within individual boxes). Cars with pre-cooled fresh produce were top iced just before shipment. Top icing added considerable dead weight to the load. Top-icing a 40-foot reefer required in over 10,000 pounds of ice. It had been postulated that as the ice melts, the resulting chilled water would trickle down through the load to continue the cooling process. It was found, however, that top-icing only benefited the uppermost layers of the cargo, and that the water from the melting ice often passed through spaces between the cartons and pallets with little or no cooling effect. It was ultimately determined that top-icing is useful only in preventing an increase in temperature, and was eventually discontinued.
(PD) Photo: U.S. Farm Security Administration - Office of War Information
Ice blocks (also called "cakes") are manually placed into reefers from a covered icing dock.[7](CC) Photo: Scotty Six
The "business end" of a mechanical ice loading system services a line of Pacific Fruit Express refrigerator cars.[8]
The typical service cycle for an ice-cooled produce reefer (generally handled as a part of a block of cars):
- The cars were cleaned with hot water or steam.
- Depending on the cargo, the cars might have undergone 4 hours of "pre-cooling" prior to loading, which entailed blowing in cold air through one ice hatch and allowing the warmer air to be expelled through the other hatches. The practice, dating back almost to the inception of the refrigerator car, saved ice and resulted in fresher cargo.
- The cars' ice bunkers were filled, either manually from an icing dock, via mechanical loading equipment, or (in locations where demand for ice was sporadic) using specially-designed field icing cars.
- The cars were delivered to the shipper for loading, and the ice was topped-off.
- Depending on the cargo and destination, the cars may have been fumigated.
- The train would depart for the eastern markets.
- The cars were reiced in transit approximately once a day.
- Upon reaching their destination, the cars were unloaded.
- If in demand, the cars would be returned to their point of origin empty. If not in demand, the cars would be cleaned and (if possible) used for a dry shipment.
Refrigerator cars required effective insulation to protect their contents from temperature extremes. "Hairfelt" derived from compressed cattle hair, sandwiched into the floor and walls of the car, was inexpensive but flawed — over its three- to four-year service life it would decay, rotting out the car's wooden partitions and tainting the cargo with a foul odor. The higher cost of other materials such as "Linofelt" (woven from flax fibers) or cork prevented their widespread adoption. Synthetic materials such as fiberglass and polystyrene, both introduced after World War II, offered the most cost-effective and practical solution.
Notes and references
- ↑ Boyle and Estrada
- ↑ White, p. 31
- ↑ White, p. 33
- ↑ White, p. 45
- ↑ Railway Review, January 29, 1887, p. 62: The subject cars travelled on the Erie, Lackawanna, New York Central, and Pennsylvania railroads.
- ↑ Source: Poor's Manual of Railroads and ICC and U.S. Census reports.
- ↑ Each block weighed between 200 and 400 pounds; crushed ice was typically used for meat cars.
- ↑ Each car will require approximately 5½ "short" tons (5 metric tons) of ice.





![(PD) Photo: U.S. Farm Security Administration - Office of War Information Ice blocks (also called "cakes") are manually placed into reefers from a covered icing dock.[7]](/wiki/images/thumb/3/3d/Men_loading_ice_blocks_into_reefers.jpg/120px-Men_loading_ice_blocks_into_reefers.jpg)
![(CC) Photo: Scotty Six The "business end" of a mechanical ice loading system services a line of Pacific Fruit Express refrigerator cars.[8]](/wiki/images/thumb/2/25/Mechanical_ice_loader.jpg/120px-Mechanical_ice_loader.jpg)