Biology/Citable Version: Difference between revisions
imported>David Tribe m (→The scope of biology: fixed links EXPLANATORY COMMENT just passed through image format emergenct caused by changes in size to primary images WARNING for future operational rules) |
imported>David Tribe |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[Image:Typhoid1902.jpg|left|thumb|300px|Biology based advances in the [[Health Sciences|health sciences]] have helped prevent many deadly infectious diseases such as [[typhoid]] in developed countries.]] | [[Image:Typhoid1902.jpg|left|thumb|300px|Biology based advances in the [[Health Sciences|health sciences]] have helped prevent many deadly infectious diseases such as [[typhoid]] in developed countries.]] | ||
Although biology addresses fundamental issues about living things, it also addresses practical questions. It is through applied biology that the | Although biology addresses fundamental issues about living things, it also addresses practical questions. It is through applied biology that the health sciences became such effective [[healing arts]] and that the world's food supply has become safer and more plentiful. | ||
Many independent [[List of biology disciplines|scientific fields]] make up biology. [[Natural history]] (the study of individual species like [[white-tailed deer]], [[sugar maple]] trees, [[box jellyfish]] and timber [[wolves]]) was one of the first areas to develop; in natural history, whole organisms are studied in an attempt to make sense of the order of nature. When plants and animals are considered in a context of how each affects the other and their environment, then the biologist's focus is on [[ecology]]. Some fields of biology focus on living organisms and their interactions within a certain realm of the earth, as in [[marine biology]]; others focus on particular aspects of living organisms, like their structure ([[anatomy]]) or function ([[physiology]]). Studies of animals form the field of [[zoology]], whereas the study of plants is called [[botany]]. [[Medicine]] and the [[health sciences]] apply biology to understanding disease and to improving health. | Many independent [[List of biology disciplines|scientific fields]] make up biology. [[Natural history]] (the study of individual species like [[white-tailed deer]], [[sugar maple]] trees, [[box jellyfish]] and timber [[wolves]]) was one of the first areas to develop; in natural history, whole organisms are studied in an attempt to make sense of the order of nature. When plants and animals are considered in a context of how each affects the other and their environment, then the biologist's focus is on [[ecology]]. Some fields of biology focus on living organisms and their interactions within a certain realm of the earth, as in [[marine biology]]; others focus on particular aspects of living organisms, like their structure ([[anatomy]]) or function ([[physiology]]). Studies of animals form the field of [[zoology]], whereas the study of plants is called [[botany]]. [[Medicine]] and the [[health sciences]] apply biology to understanding disease and to improving health. | ||
Revision as of 22:07, 26 January 2007
| Article approved by an editor (see the talk page) of the Biology Workgroup. While we have done conscientious work, we cannot guarantee that this article is wholly free of mistakes. Help improve this article further on the draft page! |
- See also Health Sciences and Healing Arts
Biology is the science of life.[1] Biologists study all aspects of Earth's living things, including the dynamic processes within them that enable them to survive. Those vital processes include the harnessing of energy and matter, the synthesis of the materials that make up the body, the healing of injuries, and the reproduction of the entire organism, among many other activities. The mysteries of life have fascinated all peoples throughout history, and curiosity about the physical beings of people, plants, and animals exists in every known society. Some of that curiosity arises from a desire to control life processes and to exploit natural resources. Pursuit of the answers has led to an understanding of organisms that has steadily improved our standard of living. Other questions come from a desire to understand nature, rather than to control it; and, in answering these, biological investigation has changed our view of the world.
Although the word 'biology' is sometimes used conversationally to refer to matters that concern flesh and blood, and living creatures, this introductory article focuses on biology as a formal science. Unlike non-scientists who are learned in natural lore, biologists formally employ the scientific method, and incorporate mathematics, physics, chemistry and other disciplines into their work.
The scope of biology
How does life begin? What features separate something that is alive from something that is dead or inanimate? Biologists use science to approach such fundamental questions, questions that also concern the philosopher, the rabbi, the imam, or the priest - as well as every person who retains a sense of wonder. The scientific theories constructed as answers rarely agree with spiritual doctrines. Some religious leaders have deplored the scientist's mechanistic approach, because it removes the requirement for active intervention by a Creator. Some notable scientists, such as Francis Crick, have welcomed biological explanations as providing a rational basis for the world, free of the need to invoke supernatural powers.[2] Other great thinkers, however, including the physicist Albert Einstein, have found no conflict between the varying teachings of science and religion; but consider divinity and the natural universe to be one and the same. In this view, mathematical equations and the language of prophets are simply two different forms of human expression, each attempting to describe a higher dimension than ordinary human experience.

Although biology addresses fundamental issues about living things, it also addresses practical questions. It is through applied biology that the health sciences became such effective healing arts and that the world's food supply has become safer and more plentiful.
Many independent scientific fields make up biology. Natural history (the study of individual species like white-tailed deer, sugar maple trees, box jellyfish and timber wolves) was one of the first areas to develop; in natural history, whole organisms are studied in an attempt to make sense of the order of nature. When plants and animals are considered in a context of how each affects the other and their environment, then the biologist's focus is on ecology. Some fields of biology focus on living organisms and their interactions within a certain realm of the earth, as in marine biology; others focus on particular aspects of living organisms, like their structure (anatomy) or function (physiology). Studies of animals form the field of zoology, whereas the study of plants is called botany. Medicine and the health sciences apply biology to understanding disease and to improving health.
The development of biology
- For more information see Citizendium's article on History of biology
This article explores just a few selected themes; those themes center on the origin of life (both 'life on earth' and the creation of a new infant) and are followed through the centuries from ancient Greece to the present day. It is apparent that a philosophy of critical thinking, investigative methods that rely on empirical evidence, and the availability of technological tools have, together, accounted for how these ideas have changed. The development of biology has drawn on many more topics, and a much larger geographical area than referred to here, but the science of biology has had a continuous thread through the centuries that began with the ancient Greek philosophers, and has generally followed the winding pattern of advancement presented here.
Biology in the ancient world
People rely on plants and animals for sustenance, and Paleolithic cave paintings show that meticulously careful observations of prey have been expressed for at least tens of millennia. Human interest in food was not limited to passive considerations since, rather than eaten as found, it was carried from place to place and processed in various ways. In Neolithic times, probably somewhere in the fertile Nile delta, more planned interactions with certain plants and their seeds led to the establishment of agriculture in many societies. When the intellectual consideration of what plants are was combined with experiments to understand their growth, then botany, the science of plants began.[3]
Anatomy and zoology both date back to at least the 4th century BCE, and the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle.[4] In the first known book that discusses how life in the womb begins, Aristotle suggested that the mother provides the substance needed to create a new life, but that the father provides this base material with the essence of the child. He thought that the female's actual physical contribution to the baby was her menstrual blood, and that the male's corresponding contribution was his semen. Aristotle used logic and observation to arrive at his theory, which, in the main, was still accepted 2000 years later. His conclusion that the woman's portion was the mere soil for the man's seed, and that the man's donation supplied all the essential humanity, was probably influenced by the assumption (in his society) that women were less highly developed than men. A popular idea that grew out of Aristotle's musings was that sperm contained a perfect miniature version of the new baby - a homunculus.
The writings of the Greek scholars were preserved and cherished by the Romans, who added literature on the structure and function of animal and human bodies. The most influential of these was Galen, who was one of the most noted physicians in Rome. Galen performed public dissections and vivisections of animals, and used his findings to try to explain human illness. His writings survived the fall of Rome, and they formed a basis for the continuing advance of medicine.
Medieval Europe and the Arab world
With the Fall of Rome, many of the great Greek and Roman works were lost in Europe. Only a few survived, and few people could read them - both the literature and the readers often cloistered together in religious orders. The University of Padua was one of the rare places in Europe where organized learning continued, and later, Padua was to become one of the seats of the Enlightenment. Arab writers, in contrast, continued the work that had been established in the Roman empire. Copies of the old manuscripts were made, and new books of empirically derived medical procedures and theory were written. Later, when the Moors invaded Europe, these books became available to scholars there.
The European Renaissance and the 'scientific method'
When the authority of the 'classical' authors (such as Aristotle and Galen), and of religious doctrine (such as the teachings of the medieval Catholic Church), on the nature of living things began to be questioned in light of actual observation and experiment, the scientific method became established. In the early 16th century, scholars had returned to reading Galen in the original Greek, and they emphasized his superiority over his later interpreters, stressing the importance of anatomy in his view of medicine. The Dutch physician Vesalius (1514-1564), although contemptuous of Galen, followed his methods to produce a new anatomy of the human body, De humani corporis fabrica (On the Workings of the Human Body). He is often called the founder of modern human anatomy. [5]
By the 17th century, the advantages of firm empirical evidence over the opinions of authorities were seen by such influential writers as Girolamo Fabrici of Italy and Francis Bacon of England (who coined the phrase knowledge is power). Rather than memorize the texts of Galen, or perform ritualized dissections as 'homage' to Galen's findings, the anatomy and physiology of animals began to be carefully explored in completely new directions. The early European biologists mapped the paths taken by the nerves and veins that traveled between organs, and analyzed their findings in an attempt to find general principles of the organization and function of the body. Theories in biology were still very preliminary, but the evidence for ideas that explained an order to living things revolutionized thinking in biology.
The Englishman William Harvey studied how embryos develop by observations of hens' eggs and by dissecting pregnant deer and other mammals. He speculated that development proceeded from one to another of the fetal forms he found, imagining that each of these forms was a stage in a continuous process. Although other of his experiments famously revealed the circulation of the blood, and identified the workings of the heart as a pump, when it came to early development he failed to see any sort of rational explanation. He could not understand how discrete organs in the developing fetus could form out of the amorphous materials in the just pregnant womb or newly fertile egg. He chose a spiritual rather than a mechanistic explanation, postulating that the soul of the new individual was derived from the placement of sperm in the female tract, invoking the gist of the old Aristotelian argument. Still, he modified Aristotle's explanation by insisting that the male and female contributions were equally important. He refuted the notion that the fetus is made up by the specific materials contributed by the male that grow because of the separate materials contributed by the female. Instead, he argued that "the material out of which the chick is formed in the egg is made at the same time it is formed" and that "out of the same material from which it is made, it is also nourished"[6]
The 18th and 19th centuries: seeing the links between life forms
As detailed examination of plant and animal species became common, and the knowledge was shared among people in many different parts of the world, similar arrangements of body structure were recognized in many different species. In the Eighteenth Century, the Swedish naturalist Carolus Linnaeus proposed a way of systematically classifying all living things. His method gives a unique name to each kind of plant and animal, and organizes them in a way that stresses similarities of physical features - based on their comparative anatomy. This naming system is still used today, and each known species has a unique name that biologists all over the world recognize. The name has two parts: genus and species, the two most refined categories in the classification scheme. The language is Latin, which was the common written language of scholars in Europe in Linnaeus' time. Human beings, for example, belong to the species Homo sapiens (Latin for 'wise man') under the family hominidae (the great apes).[7]
Although this systematic classification of living things became widely accepted, at first it did not include the idea that all living things were related. For more than a hundred years afterward, most highly educated thinkers assumed that complicated life forms (even mice!) could spring to life from a setting of inanimate objects (such as old rags and bread crumbs left in a dark corner). In the 19th century, Louis Pasteur of France showed that this common notion, spontaneous generation, was a fallacy. His life's work in bacteriology, along with the later work of the German physician Robert Koch, was important in establishing the germ theory of disease. That work helped bring the traditional practice of medicine into the health sciences and establish a scientific basis for the field of public health.
In England, Charles Darwin built on the idea of natural selection as a way to explain how diverse creatures might have common patterns of form. His observations of the variations of animal life on remote islands made him realize that individual birds, mammals and reptiles might thrive, or die, according to how well their characteristics 'fitted' their immediate habitat. He realized that individual members of any species were also different from each other in ways that made some more successful than others in producing offspring. If these kinds of differences were passed on to the offspring, then the features that made some individuals successful would become more common in each generation. From this insight, he made the bold leap in understanding to realize that perhaps, in enough time, entirely new species might arise. His theories became incorporated into the theory of evolution which suggests that all present living things descended from past living things. The existence of common ancestors would account for similar body forms among descendants, and provided a plausible basis for the wide-spread existence of patterns of very similar features among groups of plants and animals: the very patterns that Linnaeus had used to formulate his categories in classification. This idea was not entirely new, but previous proponents had found it hard to understand how such incredibly diverse life forms might come about in the few thousand years that the world was thought to have existed. By Darwin's time, advances in Earth Science had found evidence that the earth was millions of years older than had been previously suspected, and this made the idea that organisms had evolved by many small, incremental changes over thousands of generations much more plausible. Evolutionary change from ancient life was accepted by biologists as a theory that explained both the diversity of life forms and the existence of patterns of common features.
In the late 19th century, an Austrian monk, Gregor Mendel, analyzed how traits were inherited from generation to generation in garden peas, and he concluded that the male and the female parent contribute equally. Instead of a fuzzy 'blending' of the characteristics of parents, Mendel saw that discrete traits of each individual were inherited intact, apparently based on a particulate 'binary system' of alleles that coded for the quality of each of them. A pea might be wrinkled or smooth, for example, and the particular pair of alleles inherited by each pea then determined what the next generation would be like. Mendel also saw that these alleles might be either 'dominant' or 'recessive'. Together, these ideas allowed Mendel to predict the number of offspring that would have each characteristic, and the field of genetics began.
Technology advances biology
First glimpses of the microscopic world
The advance of biological thinking depended on the communication of these ideas, and also on technology. Even the communication of ideas in science has depended on technology; in a sense, the printing press was an invention that facilitated the Enlightenment, and today, electronic communication has accelerated the rate of research. The availability of technical tools for experimentation has in a large part determined the course of progress.
The features of plants and animals, for example, have been understood on an entirely different level with technological advances that provided new ways to study them. The microscope, modified by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century, revealed details of structure in the bodies of organisms that had never before been suspected. That amorphous material that Harvey could not fathom as the progenitor of organs might have seemed to him to be of a wholly different nature had he the advantage of magnification. One of the new sights that van Leeuwenhoek described was individual ova and spermatozoa. Being familiar with the theories of Aristotle, and their popular interpretation, he reported that he could actually see homunculi in the heads of the living sperm - an example of even a great scientist perceiving his expectations, rather than what was really there. Science is always influenced by past ideas. No scientist can consider any hypothesis, or analyze any set of experimental results without using his or her mind, and all the blinkers and biases that come with it - however hard the good scientist tries to shake free and be rational and objective, that mind is both consciously and unconsciously stamped with the culture that produced it.
Not only was the structure of flesh and plants seen in new detail with the microscope, but new types of organisms were also revealed: micro-organisms that could not be detected with the naked eye. [8] And so, like all important technological advances in biology, the microscope led to new ideas about living things. It was realized that tissues were composed of cells, the field of microbiology was born, and the ground was prepared for the germ theory of disease, an idea that helped bring the traditional practice of western medicine into the field of health science and modern medicine. Further developments led to the modern compound microscope by the end of the 19th century, with much higher resolution allowing the visualization of dividing cells, and the chromosomes of the nucleus.
Cell biology begins
Cell biology began around 1900, with the discovery of the chromosomes and the understanding of mitosis and meiosis. Application of Mendel's fundamental laws of heredity to genetic linkage analysis allowed the correlation of specific plant or animal traits to be ordered as gene loci in the first genetic maps.[9] The culmination of this work and evidence from cytogenetics, led to the concept of genes as heritable traits that had a physical structure in the chromosomes; in the words of Thomas Morgan "...there is an ever increasing body of information that points clearly to the chromosomes as the bearers of the Mendelian factors, it would be folly to close one's eyes to so patent a relation."[10]
Towards the mid-20th century, with the development of the electron microscope, ultra-high power examination of cells was possible and the field of cell biology began to unravel the inner architecture of cells, discovering discrete organelles that could only be seen well at such high magnification. Closer examination of the structure of the cell was combined with the ability to physically separate out the components of the cells in bulk by density and chemical properties and analyze each fraction using methods from biochemistry and biophysics. The important techniques that allowed this analysis include ultracentrifugation and gel electrophoresis. Advances in this new field of cell biology confirmed the concept that living things were composed of cell units and extended the understanding of just how cells carried out life processes.
Science differs from religious and political doctrine in at least one major manner – tenets are not to be held sacred forever, but are always there to be questioned and tested. This has proved damaging for many of them, including the homunculus theory of fetal development. With the resolving power of the electron microscopes, able to image cell structure at a magnification of tens of thousand-fold, that "little man" inside the sperm cell vanished forever.
Molecular biology, and a revolution in understanding
In the 20th century, the properties and roles of some of the large organic molecules (macromolecules) found in living things were examined. Proteins, which are one type of macromolecule, have three-dimensional shapes that give them special properties. Some proteins, known as enzymes, have specialized sites able to catalyze the chemical reactions critical for metabolism. Other proteins act as building blocks that make up the filaments that support the cytoplasm of cells, or lend such qualities as waterproofing to skin (keratin) or tensile strength to tendons (collagen). Proteins also provide an elaborately configured signaling network that guides responses to the environment. These sophisticated activities range from the selective transport of ions and food in and out of cells, to the ability of immune cells to recognize and attack only foreign germs, rather than rain friendly fire on other parts of the body. Strikingly, as protein sequences were compared between species, biologists appreciated a new variation on the old theme that research in comparative anatomy had raised three hundred years before. First, recurring anatomical patterns had been recognized in different animals, like the arrangement of bones in a bat's wing, a seal's flipper and a man's arm; and later, the molecular structures and shapes of the various families of proteins were recognized to be similarly repeating. The amino acid sequences within the protein families even show some similarity between kingdoms like bacteria and animals, confirming the idea that all living things are related.
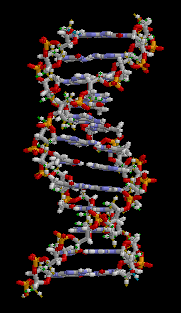
By 1953, the painstaking x-ray studies of Rosalind Franklin allowed the imagination of James Watson and Francis Crick to seize upon the structure of DNA.[11] The double helix structure of that molecule revealed how information might be coded and passed from generation to generation, by showing how the DNA molecule could act as a 'template' for the synthesis of both itself, and a related molecule, RNA. Crick and others went on to propose that small RNA molecules might serve as adaptors that could be made from such a template, and be used to assemble amino acids to build proteins.
With these advances in organic chemistry, biochemistry and molecular biology, a new view of the origin of life forms on earth emerged. "It is now widely believed that almost four billion years ago, before the first living cells, life consisted of assemblies of self-reproducing macromolecules".[12]
Studying the biochemistry of RNA and proteins involved purifying unstable compounds from sources that also contained enzymes for their breakdown. Work advanced, but successful experiments required labor-intensive manipulations that could take several days in refrigerated 'cold rooms', without substantial delay between steps. Consequently, unraveling the movement of RNA out of the nucleus to the endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes, and pinpointing the mechanics of how proteins were assembled in the cell, were heroic enterprises requiring marathon procedures (often performed by scientists dressed in parkas!).
Attention turned to the DNA sequences that coded for proteins, and the genetic traits that Mendel had observed in his peas were found to have physical correlates in the genes that these sequences provided. DNA is more stable than RNA and most proteins, and with DNA chemistry the experiments were easier. They could be performed in usual laboratory conditions and did not require the haste or continuity that RNA work had demanded. By the end of the 20th century, the technique of PCR conceived by Kary Mullis allowed experiments on tiny samples of DNA to be done very efficiently, with automated sets of reactions, and progress in molecular biology accelerated. Superfamilies of genes were found in different organisms that underlay the existence of those families of related proteins that were identified in diverse tissues and diverse species.
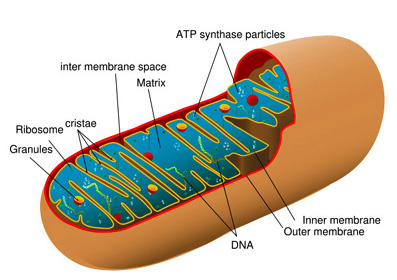
Understanding the ultrastructure of cells along with the chemical and physical properties of the organelles brought more new ideas to biology. Mitochondria are tiny organelles found in almost all cells, and these are the factories that produce energy for the cell. These mitochondria, so essential for living cells, have their own DNA and ribosomes - but their form is more similar to those of bacteria rather than mammalian cells. These observations led Lynn Margulis to propose an outlandish hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria being derived from bacteria assimilated into eukaryotic cells. Her endosymbiotic theory was finally published after being "rejected by about fifteen scientific journals".[13] [14], but is widely accepted today. These energy-producing organelles of animal cells are not the only organelles found that derived from a different life form; the chloroplasts of plant cells are another.
Back to the baby
The age-old question of how a new baby came to be born of man and woman took equally unexpected turns. The single cell from which every human develops does not receive equal genetic contributions from mother and father, after all. One of the biggest differences in the parents’ contribution to their baby is found to be cell organelles, specifically mitochondria. Each individual human being is made up of cells with "only" the mother's mitochondria and their DNA.
Even genes in the nucleus of germ cells (egg and sperm) do not always act identically in the newly fertilized egg. Some genes are marked in the germ cells to be either active or inactive in the new embryo, by the addition of chemical modifiers (like methyl groups) to the DNA. This so-called imprinting of genes by parental origin is another asymmetry that had been unsuspected. Oddly, this confirmed some of the suspicions of Aristotle after all, but in the very opposite way to that imagined by the ancients. "Genes expressed from the paternally inherited copy generally increase resource transfer to the child, whereas maternally expressed genes reduce it." [15] In other words, the genetic material provided by the father has a role slanted to provide nourishment to the fetus whereas the same genes, when inherited through the mother, act differently. The placenta grows from the same fertilized egg that builds the baby, and nourishes the new infant from the mother's womb - but it's the father's genes that are more important for the placental membrane's success in obtaining nutrients. It's as though there is a 'battle' between the father's genes and the mother's genes - as if the father's genes want the biggest baby possible, while the mother's genes want a small baby to protect the mother.[16]
The continuing story
By the end of the 20th century, progress in molecular biology had given rise to the Human Genome Project, an ambitious vision to sequence the DNA of every single human gene. Not only was that vast project, drawing on the inputs of hundreds of scientists in many different countries, completed ahead of schedule [17], but we now also have the DNA sequences of many other species with which to compare the human genome. That unexpected speed was another boon from technology and the gene sequencing projects have thrived on close collaborations with both engineering and computer sciences.
In 2006, not only can we map out how chromosomes have evolved across species, but we can use these genomic resources to trace our own distant ancestry back to the enigmatic traces of a preceding world.[18] However, for all the advances that have been made in the study of living things over the centuries, biology remains a science that has only begun to provide a basis for understanding life. The genome projects, so far from answering all our questions, instead opened up many new ones. One of the biggest surprises was the realization of how few genes it takes to make a human being - just 28,000 or so, not many more than is needed to make simple animals, and fewer than the number of genes in many plants!
The scope of these projects has been to focus on mining the genomic data for the blueprint of life. We have learned, however, that simply identifying the sequence of our DNA is not enough to really unravel our genetic code. Biologists must now start the difficult process of understanding all the ways that these genes can be processed and just how they interact with each other at the level of whole organisms. And so we come full circle, again relying on the traditional fields of biology to probe the secrets that are not apparent from knowing the genomic sequences alone.
References
- Citations
- ↑ Etymology The word 'Biology' is formed by combining two Greek words βίος (bios), meaning 'life', and λόγος (logos), meaning 'study of'. 'Biology' in its modern use was probably introduced independently by both Gottfried Reinhold Treviranus (Biologie oder Philosophie der lebenden Natur, 1802) and by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (Hydrogéologie, 1802). Although the word 'biology' is sometimes said to have been coined in 1800 by Karl Friedrich Burdach, it appears in the title of Volume 3 of Michael Christoph Hanov's Philosophiae naturalis sive physicae dogmaticae: Geologia, biologia, phytologia generalis et dendrologia, published in 1766.
- ↑ The evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins sets out the secular humanist case in 'The God Delusion' (2006) ISBN
- ↑ see Jared Diamond 'Guns, Germs, and Steel' (1997) ISBN 0-393-31755-2
- ↑ See "Aristotle's Biology" in The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy for a summary of Aristotle's biology and references to works by scholars interpreting his biological ideas.
- ↑ Nutton V (2002) Portraits of science. Logic, learning, and experimental medicine Science 295:800-1 PMID 11823624
- ↑ Van Speybroeck L et al (2002) Theories in early embryology: close connections between epigenesis, preformationism, and self-organization Ann NY Acad Sci 981:7-49 PMID 12547672
- ↑ For a more modern view on differing methods of classifying living things, see Ereshefsky M (2001) 'The Poverty of the Linnaean Hierarchy: A Philosophical Study of Biological Taxonomy' Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press. Reviewed in Nature and in Science
- ↑ Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Encyclopedia of World Biography 2nd ed. 17 Vols. Gale Research, 1998. Reproduced in Biography Resource Center. Farmington Hills, Mich.: Thomson Gale. 2006
- ↑ Sturtevant, A. H. (1913) The linear arrangement of six sex-linked factors in Drosophila.
- ↑ T. H. Morgan, A. H. Sturtevant, H. J. Muller and C. B. Bridges (1915) The Mechanism of Mendelian Heredity Henry Holt and Company
- ↑ Watson JD, Crick F (1953) The Molecular structure of Nucleic Acids: a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid Nature 171:737-738. The National Library of Medicine's PDF copy in the Francis Crick Documents Collection.
- ↑ Taylor WR (2005) Stirring the primordial soup Nature 434:705 PMID 15815609)
- ↑ Lynn Sagan, (1967) "On the origin of mitosing cells" J. Theoretical Biology 14(3):255-74. PMID 11541392
- ↑ John Brockman, The Third Culture, New York: Touchstone, 1995, 135.
- ↑ Constancia M et al (2004) Resourceful imprinting Nature 432:53-7 PMID 15525980
- ↑ Haig D. (1992) Genomic imprinting and the theory of parent-offspring conflict. Seminars in Developmental Biology 3:153-160.
- ↑ President Clinton announces the completion of the first survey of the entire human genome. June 25, 2000
- ↑ Benner SA, Ellington AD, Tauer A. (1989) Modern metabolism as a palimpsest of the RNA world. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Sep;86(18):7054-8. PMID 2476811
Notes and links
Biology today, a survey of the science of life
- For more information see Citizendium's List of biology topics, and List of important publications in biology
- Anatomy: The study of structure
- Behavior: Study of the actions and reactions of an organism
- Biochemistry: The chemistry of living things is a field of both biology and chemistry
- Biodiversity: The study of the diversity of life
- Biogeography: The study of patterns of species distribution and the processes that result in such patterns
- Botany: The study of plants and fungi (mycology)
- Cell Biology: The study of the components of cells and their interactions
- Developmental biology: The study of cell growth and interactions to form an organism
- Ecology: The study of the distribution and abundance of organisms and how they are affected by the environment
- Ethology: The scientific study of animal behavior
- Evolutionary biology: Study of the origin and descent of species, as well as their change, multiplication, and diversity over time
- Genetics: The study of the inheritance of characteristics, genes and DNA
- Immunology: Covers the study of all aspects of the immune system in all animals
- Marine Biology: The study of life in the seas and oceans
- Microbiology: The study of microorganisms (overlapping with areas of bacteriology, mycology and parasitology)
- Molecular biology: The study of molecular interactions within a cell
- Physiology: The study of the mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions of tissues and how they interact
- Systematics: The study of the diversity of organism characteristics, and how they relate via evolution
- Systems biology: The study of biological systems as-a-whole, developing quantitative models to explain, predict and control biological systems.
- Taxonomy: The principles underlying classification, often in a hierarchy
- Virology: the study of viruses, sometimes included in the field of microbiology
- Zoology: The study of animals
History of biology
- For more information see Citizendium's article on History of biology
- History of plant systematics
- History of zoology, post-Darwin
- History of zoology (before Darwin)
- History of molecular biology
- Timeline of biology and organic chemistry
Further reading
- Timothy Shanahan, The Evolution of Darwinism: Selection, Adaptation and Progress in Evolutionary Biology (2004) ISBN 0521834139
- Michel Morange, A History of Molecular Biology ISBN 0−674−39855−6; see review here
- Stephen Jay Gould, Full House: The Spread of Excellence From Plato to Darwin (1996), ISBN 0-517-70394-7 (Released outside North America as Life's Grandeur: The Spread of Excellence From Plato to Darwin (1996), ISBN 0-099-89360-6)
- Richard Dawkins, The Ancestor's Tale (2004) ISBN 0-618-00583-8; Audio (2005) ISBN 0-7528-7321-0
Selected external links
- The American Institute of Biological Sciences (ABIBS) Virtual Library is free to all visitors
- The Bio-Web reviews and gives access to information in Cell and Molecular Biology, includes "news" in plain language
- Cell and Molecular Biology Online is a resource for professionals that includes links and some information for all
- Kimball's Biology Pages are a online elementary college biology textbook, based on the author's 1996 printed edition.