Penicillin V: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk m (→Chemistry) |
imported>Jeffrey Scott Bernstein m ("it" was missing) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
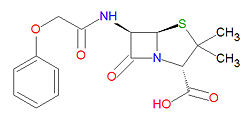
[[Image:Penicillin V structure.jpg|right|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Penicillin V structure.jpg/credit|{{Penicillin V structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Penicillin V]] | [[Image:Penicillin V structure.jpg|right|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Penicillin V structure.jpg/credit|{{Penicillin V structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Penicillin V]] | ||
'''Penicillin V''', or '''phenoxymethyl penicillin''', is a broad-spectrum, beta-[[lactam]]-based [[antibiotic]] used to treat mild to severe infections due to gram-positive bacteria. | '''Penicillin V''', or '''phenoxymethyl penicillin''', is a broad-spectrum, beta-[[lactam]]-based [[antibiotic]] used to treat mild to severe infections due to gram-positive bacteria. It is used to treat dental, hear, middle ear, respiratory tract and skin infections, and can also treat [[rheumatic fever|rheumatic]] and [[scarlet fever]]s. | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
Revision as of 10:39, 10 March 2008
Penicillin V, or phenoxymethyl penicillin, is a broad-spectrum, beta-lactam-based antibiotic used to treat mild to severe infections due to gram-positive bacteria. It is used to treat dental, hear, middle ear, respiratory tract and skin infections, and can also treat rheumatic and scarlet fevers.
Mechanism of action
Like other penicillin-like drugs, penicillin V works by binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins in bacterial cell walls and blocking the final cross-linking step in the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. This induces autolysis of the bactertial cells by autolysins.
Chemistry
Penicillin V is stable against degradation by beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases. Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[[2-(phenoxy)acetyl]amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has molecular formula C16H18N2O5S (MM = 350.3895 g/mol).
Drug interactions
Tetracycline and its derivatives demeclocycline, doxycycline, methacycline, minocycline, oxytetracycline, rolitetracycline, and tetracycline are antagonists of penicillins. The effects of oral contraceptives, including [[ethinyl estradiol] and mestranol are decreased when using penicillin. Penicillins increases the effect and toxicity of methotrexate.[1]
Synonyms and brand names
synonyms
- Fenossimetilpenicillina
- Fenoximetilpenicilina
- Penicillin Phenoxymethyl
- Penicillin V Potassium
- Phenoxymethylpenicillinic Acid
- Phenoxymethylpenicillinic Acid Potassium Salt
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin Potassium
- Phenoxymethylenepenicillinic Acid
- Phenoxymethyl Penicillin
- Phenoximethylpenicillinum
Brand names
- Acipen V®
- Apopen®
- Beepen-Vk®
- Beromycin®
- Betapen-Vk®
- Calcipen®
- Compocillin V®
- Crystapen V®
- Distaquaine V®
- Eskacillian V®
- Eskacillin V®
- Fenacilin®
- Fenospen®
- Fenoxypen®
- Ledercillin Vk®
- Meropenin®
- Oracillin®
- Oratren®
- Ospen®
- Pen-Oral®
- Pen-V®
- Pen-Vee®
- Pen-Vee K®
- Penapar-Vk®
- Penicillin Vk®
- Penicillin-Vk®
- Pfizerpen Vk®
- Phenocillin®
- Phenomycilline®
- Phenopenicillin®
- Robicillin®
- Rocilin®
- Stabicillin®
- Uticillin Vk®
- V-Cil®
- V-Cillin®
- V-Cillin K®
- V-Cylina®
- V-Cyline®
- V-Tablopen®
- Vebecillin®
- Veetids®
- Veetids '125'®
- Veetids '250'®
- Veetids '500'®
External links
- Penicillin V - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Template:MedMaster
- Template:DrugBank