Ampicillin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk m (→External links) |
imported>David E. Volk (four columns for brand names Chem infobox) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
[[Image:Ampicillin structure.jpg| | |||
{{Chem infobox | |||
|align=right | |||
|image=[[Image:Ampicillin structure.jpg|center|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Ampicillin structure.jpg/credit|{{Ampicillin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}]] | |||
|width=250px | |||
|molname=ampicillin | |||
|synonyms='''aminobenzylpenicillin''' | |||
|molformula= C<sub>16</sub>H<sub>19</sub>N<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>S | |||
|molmass= 349.4048 | |||
|uses=antibiotic drug | |||
|properties=beta-lactam | |||
|hazards=see drug interactions | |||
|iupac= see chemistry section | |||
|casnumber=69-53-4 | |||
}} | |||
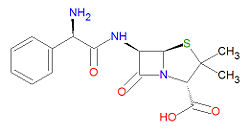
'''Ampicillin''', or '''aminobenzylpenicillin''', is a broad spectrum [[antibiotic]] and a derivative of [[penicillin]]. It is used to treat infections of [[E. coli]], [[P. mirabilis]], [[enterococci]], [[Shigella]], [[S. typhosa]] and other [[Salmonella]], nonpenicillinase-producing [[N. gononhoeae]], [[H. influenzae]], [[staphylococci]], and [[streptococci]] including [[streptoc]]. It is also widely used in [[molecular biology]] labs during the over-expression of proteins in bacterial cells that are tolerant of ampicillin. This ensures that only the bacteria of interest grow in the media and produce the protein of interest. | '''Ampicillin''', or '''aminobenzylpenicillin''', is a broad spectrum [[antibiotic]] and a derivative of [[penicillin]]. It is used to treat infections of [[E. coli]], [[P. mirabilis]], [[enterococci]], [[Shigella]], [[S. typhosa]] and other [[Salmonella]], nonpenicillinase-producing [[N. gononhoeae]], [[H. influenzae]], [[staphylococci]], and [[streptococci]] including [[streptoc]]. It is also widely used in [[molecular biology]] labs during the over-expression of proteins in bacterial cells that are tolerant of ampicillin. This ensures that only the bacteria of interest grow in the media and produce the protein of interest. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 22: | ||
Ampicillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used to eliminate susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. Like penicillin, ampicillin inhibits the last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins in the bacterial cell wall. | Ampicillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used to eliminate susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. Like penicillin, ampicillin inhibits the last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins in the bacterial cell wall. | ||
Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>16</sub>H<sub>19</sub>N<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>S. | Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>16</sub>H<sub>19</sub>N<sub>3</sub>O<sub>4</sub>S, giving it a molecular mass of 349.4048 g/mol. | ||
== Synonyms of ampicillin == | == Synonyms of ampicillin == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 44: | ||
== Brand names of ampicillin == | == Brand names of ampicillin == | ||
{{col-begin}} | |||
{{col-break|width=25%}} | |||
# AB-PC | # AB-PC | ||
# Ab-Pc Sol | # Ab-Pc Sol | ||
| Line 57: | Line 76: | ||
# Ampivet | # Ampivet | ||
# Amplacilina | # Amplacilina | ||
{{col-break|width=25%}} | |||
# Amplin | # Amplin | ||
# Amplipenyl | # Amplipenyl | ||
| Line 85: | Line 108: | ||
# Novo-Ampicillin | # Novo-Ampicillin | ||
# Nuvapen | # Nuvapen | ||
{{col-break|width=25%}} | |||
# Olin Kid | # Olin Kid | ||
# Omnipen | # Omnipen | ||
| Line 113: | Line 139: | ||
# Principen '125' | # Principen '125' | ||
# Principen '250' | # Principen '250' | ||
{{col-break|width=25%}} | |||
# Principen '500' | # Principen '500' | ||
# Qidamp | # Qidamp | ||
| Line 141: | Line 170: | ||
# Viccillin S | # Viccillin S | ||
# Wypicil | # Wypicil | ||
{{col-end}} | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 3 April 2008
|
| |||||||
| ampicillin | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Ampicillin, or aminobenzylpenicillin, is a broad spectrum antibiotic and a derivative of penicillin. It is used to treat infections of E. coli, P. mirabilis, enterococci, Shigella, S. typhosa and other Salmonella, nonpenicillinase-producing N. gononhoeae, H. influenzae, staphylococci, and streptococci including streptoc. It is also widely used in molecular biology labs during the over-expression of proteins in bacterial cells that are tolerant of ampicillin. This ensures that only the bacteria of interest grow in the media and produce the protein of interest.
Ampicillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used to eliminate susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. Like penicillin, ampicillin inhibits the last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins in the bacterial cell wall.
Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C16H19N3O4S, giving it a molecular mass of 349.4048 g/mol.
Synonyms of ampicillin
- Ampicilline
- Ampicillinum
- Ampicilline
- Ampicillina
- Ampicillin
- Ampicillin Trihydrate
- Ampicillin Sodium
- Ampicillin Base
- Ampicillin Anhydrous
- Ampicillin Anhydrate
- Ampicillin Acid
- Ampicilina
- Anhydrous Ampicillin
- Bayer 5427
- D-Ampicillin
- Aminobenzylpenicillin
Brand names of ampicillin
|
|
|
|
External links
- Ampicillin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Template:MedMaster
- Template:DrugBank