Amprenavir: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk m (→External Links) |
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-* {{CZMed +{{CZMed)) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
{{CZMed}} | |||
Revision as of 01:27, 4 June 2009
|
| |||||||
| amprenavir | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | HIV | ||||||
| Properties: | protease inhibitor | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
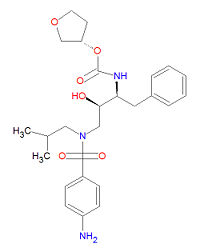
Amprenavir, also called AMP, AMV, APV and VX-478, is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. Protease inhibitors block HIV-1 protease, an enzyme required for the proteolytic cleavage of the viral polyprotein precursors into the individual functional proteins found in infectious HIV-1. Protease inhibitors are almost always used in combination with at least two other anti-HIV drugs. Its IUPAC chemical name is [(3S)-oxolan-3-yl] N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-
hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate.
Brand Names
- Agenerase®
- Prozei®
- Vertex®
External Links
The most up-to-date information about Amprenavir and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Amprenavir - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Amprenavir - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Amprenavir - Detailed information from DrugBank.