Mevalonate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (stub and structure) |
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:Mevalonate structure.jpg|right|thumb|150px|{{|{{Mevalonate structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|Mevalonate.]] | [[Image:Mevalonate structure.jpg|right|thumb|150px|{{|{{Mevalonate structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|Mevalonate.]] | ||
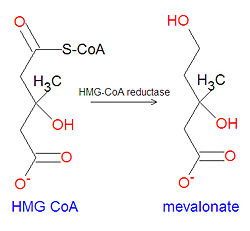
'''Mevalonate''' is a key chemical precursor in the biosynthesis of [[cholesterol]]. The statin drugs used to lower cholesterol are [[Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor|HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor]]s that work by inhibiting the synthesis of mevalonate from [[3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl CoA]] (HMG-CoA). | '''Mevalonate''' is a key chemical precursor in the biosynthesis of [[cholesterol]]. The statin drugs used to lower cholesterol are [[Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor|HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor]]s that work by inhibiting the synthesis of mevalonate from the reduction of [[3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl CoA]] (HMG-CoA). | ||
[[Image:Mevalonate synthesis.jpg|left|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Mevalonate synthesis.jpg/credit|{{Mevalonate synthesis.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Biosynthesis of mevalonate from HMG CoA.]] | |||
Revision as of 13:16, 24 January 2008
Mevalonate is a key chemical precursor in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. The statin drugs used to lower cholesterol are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors that work by inhibiting the synthesis of mevalonate from the reduction of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA).