User:John R. Brews/Draft: Difference between revisions
imported>John R. Brews (→Types) |
imported>John R. Brews (→Types) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*Tunnel diode: Like the Zener diode, the tunnel diode (or Esaki diode)is made up of heavily doped ''n-'' and ''p''-type layers with a very abrupt transition between the two types. Conduction takes place by electron tunneling. | *Tunnel diode: Like the Zener diode, the tunnel diode (or Esaki diode)is made up of heavily doped ''n-'' and ''p''-type layers with a very abrupt transition between the two types. Conduction takes place by electron tunneling. | ||
*Light-emitting diode: The [[Light Emitting Diode|light-emitting diode]] is designed to convert electrical current into light. | *Light-emitting diode: The [[Light Emitting Diode|light-emitting diode]] is designed to convert electrical current into light. | ||
==Operation== | |||
Here, the operation of the simple ''pn'' junction diode is considered. | |||
Revision as of 12:37, 9 January 2011
A semiconductor diode is a two-terminal device that conducts current in only one direction, made by joining a p-type semiconducting layer to an n-type semiconducting layer.
Electrical behavior
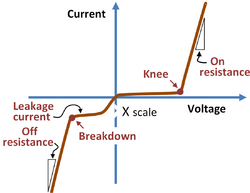
The ideal diode has zero resistance for the forward bias polarity, and infinite resistance (conducts zero current) for the reverse voltage polarity. The pn-diode is not ideal. As shown in the figure, the diode does not conduct appreciably until a nonzero knee voltage (also called the turn-on voltage) is reached. Above this voltage the slope of the current-voltage curve is not infinite, but exhibits a nonzero forward resistance. In the reverse direction the diode conducts a nonzero leakage current (exaggerated by a smaller scale in the figure) and at a sufficiently large reverse voltage below the breakdown voltage the current increases very rapidly with more negative reverse voltages.
Types
Semiconductor diodes come in a large variety of types:
- pn-diode: The pn junction diode consists of an n-type semiconductor joined to a p-type semiconductor.
- Zener diode: The Zener diode is a special type of pn-diode made to operate in the reverse breakdown region, and used often as a voltage regulator. The breakdown voltage in these didoes is sometimes called the Zener voltage. Depending upon the voltage range designed for, the diode may break down by either Zener breakdown, an electron tunneling behavior, or by avalanche breakdown.
- Schottky diode: The Schottky diode is made using a metal such as aluminum or platinum, on a lightly doped semiconductor substrate.
- Metal-oxide varistor: The varistor is intended to provide a voltage controlled resistance. Its resistance under small voltage variations is set by the choice of a bias voltage.
- Tunnel diode: Like the Zener diode, the tunnel diode (or Esaki diode)is made up of heavily doped n- and p-type layers with a very abrupt transition between the two types. Conduction takes place by electron tunneling.
- Light-emitting diode: The light-emitting diode is designed to convert electrical current into light.
Operation
Here, the operation of the simple pn junction diode is considered.