Benjamin Franklin/Citable Version: Difference between revisions
imported>D. Matt Innis m (Protected "Benjamin Franklin": approved version [edit=sysop:move=sysop]) |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Pennsylvania" to "Pennsylvania") |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
[[image:Benfranklin.jpg|250px|thumb|Portrait of Benjamin Franklin (circa 1785) by [[Joseph Siffred Duplessis]] ]] | [[image:Benfranklin.jpg|250px|thumb|Portrait of Benjamin Franklin (circa 1785) by [[Joseph Siffred Duplessis]] ]] | ||
'''Benjamin Franklin''' (1706-1790), known as "the First American," was an American statesman whose efforts were critical to the success of the [[American Revolution]] and the unification of the [[Thirteen Colonies|13 colonies]] into a new nation. Serving as the American minister to France along with [[John Adams]], he secured decisive military and financial support during the Revolution, while asserting the values of democracy and [[Republicanism, U.S.|republicanism]]. He assisted [[Thomas Jefferson]] in writing the [[Declaration of Independence]] in 1776 and helped legitimize the [[U.S. Constitution]] in 1787. His effective diplomacy, creative nationalism, promotion of civic virtue and devotion to republicanism earned him high rank as a [[Founding Fathers of the United States|Founding Father]]. | '''Benjamin Franklin''' (1706-1790), known as "the First American," was an American statesman whose efforts were critical to the success of the [[American Revolution]] and the unification of the [[Thirteen Colonies|13 colonies]] into a new nation. Serving as the American minister to France along with [[John Adams]], he secured decisive military and financial support during the Revolution, while asserting the values of democracy and [[Republicanism, U.S.|republicanism]]. He assisted [[Thomas Jefferson]] in writing the [[U.S. Declaration of Independence]] in 1776 and helped legitimize the [[U.S. Constitution]] in 1787. His effective diplomacy, creative nationalism, promotion of civic virtue and devotion to republicanism earned him high rank as a [[Founding Fathers of the United States|Founding Father]]. | ||
Franklin was also a world class scientist during | Franklin was also a world-class scientist during [[The Enlightenment]], famed for his discoveries in [[electricity]] and his invention of the [[lightning]] rod. He was also a noted printer and civic leader in Philadelphia.{{TOC|left}} | ||
==Early Life== | ==Early Life== | ||
Franklin was born on January 17, 1706 in [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston]], [[Massachusetts]], into a [[Congregationalist]] family. His father was Josiah Franklin, a soap and candle maker, who was twice married with 17 children. Benjamin briefly worked as an apprentice under his father before being apprenticed at age 12 to his brother James Franklin, one of the first American printers. James created the first independent newspaper in the colonies, a weekly publication called the ''[[New England Courant]]''. The ''Courant'' frequently published pseudonymous essays discussing all manner of contemporary issues, which Franklin developed an interest in. He created his own pseudonym, Silence Dogood, a prudish, rural widow, and submitted essays to the ''Courant'' for publication. He published 14 essays between April and October 1722. Franklin's identity had been kept secret from even his brother, however, he decided to reveal himself after his final essay. James, who was jealous of his talented younger brother, began writing his own essays which focused their attacks on religion. The ''Courant'' drew the anger of the local authorities, who prohibited James from publishing it. In order to continue printing, James released his brother from his apprenticeship and named him the publisher; Benjamin used this release to his advantage, escaping the control of his overbearing brother by running away to [[Philadelphia]], [[Pennsylvania]], at the age of 17. | Franklin was born on January 17, 1706 in [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston]], [[Massachusetts (U.S. state)|Massachusetts]], into a [[Congregationalist]] family. His father was Josiah Franklin, a soap and candle maker, who was twice married with 17 children. Benjamin briefly worked as an apprentice under his father before being apprenticed at age 12 to his brother James Franklin, one of the first American printers. James created the first independent newspaper in the colonies, a weekly publication called the ''[[New England Courant]]''. The ''Courant'' frequently published pseudonymous essays discussing all manner of contemporary issues, which Franklin developed an interest in. He created his own pseudonym, Silence Dogood, a prudish, rural widow, and submitted essays to the ''Courant'' for publication. He published 14 essays between April and October 1722. Franklin's identity had been kept secret from even his brother, however, he decided to reveal himself after his final essay. James, who was jealous of his talented younger brother, began writing his own essays which focused their attacks on religion. The ''Courant'' drew the anger of the local authorities, who prohibited James from publishing it. In order to continue printing, James released his brother from his apprenticeship and named him the publisher; Benjamin used this release to his advantage, escaping the control of his overbearing brother by running away to [[Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia]], [[Pennsylvania (U.S. state)|Pennsylvania]], at the age of 17. | ||
==Printer and Civic Leader== | ==Printer and Civic Leader== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
In late 1732, Franklin began writing and publishing ''[[Poor Richard's Almanack]]'', under the guise of Poor Richard Saunders and his wife, Bridget. Its purpose was to provide practical knowledge to the common man while interjecting a rich dose of humor. Franklin had a knack for rewording old proverbs in a wittier manner, and it was his wit that was instrumental in separating ''Poor Richard's'' from other almanacs being printed in Philadelphia. The ''Almanack'' also served as an outlet for Franklin's desire toward self improvement and helping others. It became an annual publication from 1732 to 1758. | In late 1732, Franklin began writing and publishing ''[[Poor Richard's Almanack]]'', under the guise of Poor Richard Saunders and his wife, Bridget. Its purpose was to provide practical knowledge to the common man while interjecting a rich dose of humor. Franklin had a knack for rewording old proverbs in a wittier manner, and it was his wit that was instrumental in separating ''Poor Richard's'' from other almanacs being printed in Philadelphia. The ''Almanack'' also served as an outlet for Franklin's desire toward self improvement and helping others. It became an annual publication from 1732 to 1758. | ||
{{Image|Bfranklin_penn.jpg|left|300px|Statue of Benjamin Franklin on the University of Pennsylvania campus.}} | |||
In 1758, the year in which he ceased writing for the ''Poor Richard's Almanack'', he printed [[Father Abraham's Sermon]]. [[The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin|Franklin's autobiography]], published after his death, is regarded as one of the classics of the genre and is still quoted extensively by many essayists. | In 1758, the year in which he ceased writing for the ''Poor Richard's Almanack'', he printed [[Father Abraham's Sermon]]. [[The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin|Franklin's autobiography]], published after his death, is regarded as one of the classics of the genre and is still quoted extensively by many essayists. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
Franklin's great scientific achievement came in his experiments and theories regarding [[electricity]]. He was first intrigued by the concept after meeting Archibald Spencer and witnessing his demonstrations on the creation of static electricity. In 1747, Spencer donated a glass tube and information on generating electricity to the Library Company. Franklin had several of these glass devices made for his experiments. He theorized that electricity was a "fluid" with opposing charges. His theory suggests that when a "positive" charge is created, a "negative" charge is created as well. This principle became known as the [[conservation of charge]]. He also began using [[Leyden jar|Leyden jars]], a glass jar with foil on the outside and a conductor such as water or metal on the inside that could be charged with a wire. Franklin determined that the charge was not stored in the conductor, as was previously thought, but was held in the glass. To hold a bigger charge he wired multiple Leyden jars together and flanked them with metal into what he called a battery. This was not a battery in the modern sense, rather the Leyden jar was an early form of the [[capacitor]].<ref>The charge is contained in a layer of the conductor facing the glass and the glass (the [[dielectricum]]) increases the [[capacitance]] of the jar (amount of charge that can be held).</ref> | Franklin's great scientific achievement came in his experiments and theories regarding [[electricity]]. He was first intrigued by the concept after meeting Archibald Spencer and witnessing his demonstrations on the creation of static electricity. In 1747, Spencer donated a glass tube and information on generating electricity to the Library Company. Franklin had several of these glass devices made for his experiments. He theorized that electricity was a "fluid" with opposing charges. His theory suggests that when a "positive" charge is created, a "negative" charge is created as well. This principle became known as the [[conservation of charge]]. He also began using [[Leyden jar|Leyden jars]], a glass jar with foil on the outside and a conductor such as water or metal on the inside that could be charged with a wire. Franklin determined that the charge was not stored in the conductor, as was previously thought, but was held in the glass. To hold a bigger charge he wired multiple Leyden jars together and flanked them with metal into what he called a battery. This was not a battery in the modern sense, rather the Leyden jar was an early form of the [[capacitor]].<ref>The charge is contained in a layer of the conductor facing the glass and the glass (the [[dielectricum]]) increases the [[capacitance]] of the jar (amount of charge that can be held).</ref> | ||
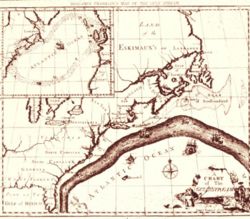
{{Image|BF_Gulf_stream_map.jpg|right|250px|Franklin's Chart of the Gulf Stream}} | |||
Franklin began noticing the similar properties of [[lightning]] and electrical sparks, which led to his most famous experiment. In 1750, Franklin outlined his proposal in two letters to Peter Collinson, which were published and presented to the Royal Society in London. On May 10, 1752 French scientist [[Thomas-François D'Alibard]] successfully performed Franklin's experiment outside of Paris. In June, before word of success had crossed the Atlantic, Franklin performed his kite and key experiment with his son, William, with similar success, which has become a popular part of American folklore.<ref>Theater of Electricity Exhibit, "[http://www.mos.org/sln/toe/kite.html Franklin's Kite]" (Museum of Science, Boston; last accessed March 6, 2009); {{cite web | Franklin began noticing the similar properties of [[lightning]] and electrical sparks, which led to his most famous experiment. In 1750, Franklin outlined his proposal in two letters to Peter Collinson, which were published and presented to the Royal Society in London. On May 10, 1752 French scientist [[Thomas-François D'Alibard]] successfully performed Franklin's experiment outside of Paris. In June, before word of success had crossed the Atlantic, Franklin performed his kite and key experiment with his son, William, with similar success, which has become a popular part of American folklore.<ref>Theater of Electricity Exhibit, "[http://www.mos.org/sln/toe/kite.html Franklin's Kite]" (Museum of Science, Boston; last accessed March 6, 2009); {{cite web | ||
|url=http://www.thebakken.org/electricity/franklin-kite.html | |url=http://www.thebakken.org/electricity/franklin-kite.html | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
===Continental Congress=== | ===Continental Congress=== | ||
Upon his return, Franklin was elected to the [[Second Continental Congress]]. On July 21, he presented plans for the [[Articles of Confederation]], similar to his Albany Plan, which called for a strong central government and a congress with proportional representation. Most of his ideas were not included in the version Congress adopted in 1777. As popular sentiment for independence grew in early 1776, Franklin, along with [[Thomas Jefferson]], [[John Adams]], [[Roger Sherman]], and [[Robert Livingston]], was selected by Congress to draft the [[Declaration of Independence]]. The document was written primarily by Jefferson, with Franklin offering his editorial commentary. With America formally declaring it's sovereignty and the war going poorly, in December of 1776 Franklin was sent to France, along with [[Silas Deane]] and [[Arthur Lee]], to secure aid for the rebellion. | Upon his return, Franklin was elected to the [[Second Continental Congress]]. On July 21, he presented plans for the [[Articles of Confederation]], similar to his Albany Plan, which called for a strong central government and a congress with proportional representation. Most of his ideas were not included in the version Congress adopted in 1777. As popular sentiment for independence grew in early 1776, Franklin, along with [[Thomas Jefferson]], [[John Adams]], [[Roger Sherman]], and [[Robert Livingston]], was selected by Congress to draft the [[U.S. Declaration of Independence]]. The document was written primarily by Jefferson, with Franklin offering his editorial commentary. With America formally declaring it's sovereignty and the war going poorly, in December of 1776 Franklin was sent to France, along with [[Silas Deane]] and [[Arthur Lee]], to secure aid for the rebellion. | ||
===Minister to France=== | ===Minister to France=== | ||
Franklin arrived to great fanfare in France. Already popular for his lightning experiment, his flirtatious manner and wit made him a favorite among the courtiers. Franklin also proved himself to be a crafty diplomat. By the end of 1777, after the American victory at [[Battle of Saratoga|Saratoga]], the French favored an alliance with the Americans which was dismissed by their ally [[Spain]]. Franklin played on the traditional hatred between the British and the French, using the press to get his messages across. On February 5, 1778 America officially signed a treaty of alliance with France with the stipulation that they must have France's approval to negotiate peace with England. French aid proved to be critical to the Americans success, most notably in October 1781 at [[Siege of Yorktown|Yorktown]] in which the support of French naval forces and ground troops caused the British to surrender. This gave America the leverage it needed to negotiate peace with England and Franklin, along with [[John Jay]] and John Adams, negotiated the [[Treaty of Paris (1783)|Treaty of Paris]]. | Franklin arrived to great fanfare in France. Already popular for his lightning experiment, his flirtatious manner and wit made him a favorite among the courtiers. Franklin also proved himself to be a crafty diplomat. By the end of 1777, after the American victory at [[Battle of Saratoga|Saratoga]], the French favored an alliance with the Americans which was dismissed by their ally [[Spain]]. Franklin played on the traditional hatred between the British and the French, using the press to get his messages across. On February 5, 1778 America officially signed a treaty of alliance with France with the stipulation that they must have France's approval to negotiate peace with England. French aid proved to be critical to the Americans success, most notably in October 1781 at [[Siege of Yorktown|Yorktown]] in which the support of French naval forces and ground troops caused the British to surrender. This gave America the leverage it needed to negotiate peace with England and Franklin, along with [[John Jay]] and John Adams, negotiated the [[Treaty of Paris (1783)|Treaty of Paris]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:37, 5 August 2023

Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790), known as "the First American," was an American statesman whose efforts were critical to the success of the American Revolution and the unification of the 13 colonies into a new nation. Serving as the American minister to France along with John Adams, he secured decisive military and financial support during the Revolution, while asserting the values of democracy and republicanism. He assisted Thomas Jefferson in writing the U.S. Declaration of Independence in 1776 and helped legitimize the U.S. Constitution in 1787. His effective diplomacy, creative nationalism, promotion of civic virtue and devotion to republicanism earned him high rank as a Founding Father.
Franklin was also a world-class scientist during The Enlightenment, famed for his discoveries in electricity and his invention of the lightning rod. He was also a noted printer and civic leader in Philadelphia.
Early Life
Franklin was born on January 17, 1706 in Boston, Massachusetts, into a Congregationalist family. His father was Josiah Franklin, a soap and candle maker, who was twice married with 17 children. Benjamin briefly worked as an apprentice under his father before being apprenticed at age 12 to his brother James Franklin, one of the first American printers. James created the first independent newspaper in the colonies, a weekly publication called the New England Courant. The Courant frequently published pseudonymous essays discussing all manner of contemporary issues, which Franklin developed an interest in. He created his own pseudonym, Silence Dogood, a prudish, rural widow, and submitted essays to the Courant for publication. He published 14 essays between April and October 1722. Franklin's identity had been kept secret from even his brother, however, he decided to reveal himself after his final essay. James, who was jealous of his talented younger brother, began writing his own essays which focused their attacks on religion. The Courant drew the anger of the local authorities, who prohibited James from publishing it. In order to continue printing, James released his brother from his apprenticeship and named him the publisher; Benjamin used this release to his advantage, escaping the control of his overbearing brother by running away to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, at the age of 17.
Printer and Civic Leader
Upon his arrival in Philadelphia, Franklin found work at the print shop of Samuel Keimer. He became acquainted with the governor of the colony, William Keith, who persuaded Franklin that he needed to go into business for himself and offered him letters of credit in London to purchase equipment. When he arrived in London in December 1724, he learned that Keith's letters of credit were useless. The next two years were spent working in the local print shops. In July 1726, he returned to Philadelphia with the aid of Thomas Denham, a Quaker merchant he befriended on his trip to London. Denham paid for Franklin's trip in exchange for Franklin's work in his general store. Denham passed away shortly after returning to Philadelphia, and so Franklin resumed his career as a print shop apprentice. In 1728, Franklin partnered with his fellow apprentice, Hugh Meredith, and opened their own print shop. Franklin soon bought out Meredith and began publishing The Pennsylvania Gazette, which he purchased from his former employer, Samuel Keimer.
In September 1730, Franklin entered a common law marriage with Deborah Read. No legal ceremony was possible because Deborah was still legally married; her husband had deserted to avoid paying a debt.[1] Around this time, Franklin fathered an illegitimate son by an unknown woman, and William Franklin was raised in his new household.[2] In 1732, Deborah gave birth to their first son, Francis, who died of smallpox at the age of 4, leading Franklin to be advocate of inoculations. Sarah Franklin, who went by Sally, was born 11 years later in 1743.
In late 1732, Franklin began writing and publishing Poor Richard's Almanack, under the guise of Poor Richard Saunders and his wife, Bridget. Its purpose was to provide practical knowledge to the common man while interjecting a rich dose of humor. Franklin had a knack for rewording old proverbs in a wittier manner, and it was his wit that was instrumental in separating Poor Richard's from other almanacs being printed in Philadelphia. The Almanack also served as an outlet for Franklin's desire toward self improvement and helping others. It became an annual publication from 1732 to 1758.
In 1758, the year in which he ceased writing for the Poor Richard's Almanack, he printed Father Abraham's Sermon. Franklin's autobiography, published after his death, is regarded as one of the classics of the genre and is still quoted extensively by many essayists.
Throughout the 1730's, Franklin further demonstrated his civic-mindedness by creating and organizing community services in Philadelphia. He did this with the help of the Junto, also known as the Leather Apron Club, a group of friends and fellow tradesmen that had formed a social club in 1727. He established America's first subscription library, the Library Company of Philadelphia, in 1731. In 1736, he organized the first volunteer fire department, the Union Fire Company. In 1743, he expanded the idea of the Junto to all of the colonies by organizing the American Philosophical Society. In January 1751, Franklin helped establish the College of Philadelphia (now the University of Pennsylvania) and served on the board of trustees until 1790. Shortly afterward he helped fund the Pennsylvania Hospital. He was also an advocate for creating a more organized police force, which he was eventually able to do by 1752.
Perhaps his most radical idea of the time was to create a Pennsylvania Militia independent of the colonial government. The numerous French and Indian Wars were a threat to the safety of Pennsylvania, as the French in Canada organized Indians who raided the frontier settlements. The Pennsylvania government was controlled by the Penn family and the Quakers, who refused to organize any military defense. In November 1747, Franklin wrote a pamphlet called Plain Truth in which he advocated the creation of a defense force since the government would not do so. The pamphlet was enthusiastically received, and Franklin organized and helped the colony fund a 10,000 man militia, which generated for him enormous popularity.
Although he was a deist and rejected the idea of a personal God involved in human affairs, Franklin believed in the importance of religion for fostering a positive social atmosphere. He stressed that morality and performing good deeds were more important than just faith alone. Franklin published the sermons of the Methodist itinerant preacher George Whitefield, who captivated Philadelphians, generating a renewed enthusiasm toward religion in the First Great Awakening.
By the late 1740's, Franklin's printing business had expanded throughout the colonies. In 1748, he retired from the printing business and passed control of his operations to David Hall, while maintaining partial ownership.
Scientist and Inventor
During the 1740's, Franklin spent much of his free time performing experiments and using the results to invent and improve practical things. In 1744, he designed the "Pennsylvania Fireplace" (commonly known as the Franklin Stove), a wood burning stove that fit inside a fireplace which helped to maximize heat while producing less smoke. The stove was not as practical as he had hoped, but it laid the groundwork for more efficient wood burning stoves. In a move typical of his civic minded behavior, he declined what would have been a lucrative patent on the stove.
Franklin's great scientific achievement came in his experiments and theories regarding electricity. He was first intrigued by the concept after meeting Archibald Spencer and witnessing his demonstrations on the creation of static electricity. In 1747, Spencer donated a glass tube and information on generating electricity to the Library Company. Franklin had several of these glass devices made for his experiments. He theorized that electricity was a "fluid" with opposing charges. His theory suggests that when a "positive" charge is created, a "negative" charge is created as well. This principle became known as the conservation of charge. He also began using Leyden jars, a glass jar with foil on the outside and a conductor such as water or metal on the inside that could be charged with a wire. Franklin determined that the charge was not stored in the conductor, as was previously thought, but was held in the glass. To hold a bigger charge he wired multiple Leyden jars together and flanked them with metal into what he called a battery. This was not a battery in the modern sense, rather the Leyden jar was an early form of the capacitor.[3]
Franklin began noticing the similar properties of lightning and electrical sparks, which led to his most famous experiment. In 1750, Franklin outlined his proposal in two letters to Peter Collinson, which were published and presented to the Royal Society in London. On May 10, 1752 French scientist Thomas-François D'Alibard successfully performed Franklin's experiment outside of Paris. In June, before word of success had crossed the Atlantic, Franklin performed his kite and key experiment with his son, William, with similar success, which has become a popular part of American folklore.[4] This led to the invention of lightning rods, which became widespread in the colonies, as well as Europe, bringing international fame to Franklin almost overnight. In 1753, he received honorary degrees from both Harvard and Yale, and the Royal Society in London awarded him the prestigious Copley Medal.
In 1784, King Louis XVI appointed Franklin chairman of the French Royal Commission to scientifically examine Franz Mesmer's theory of animal magnetism. Mesmer believed he could use naturally occurring "magnetic fluids" to cure ailments. After running several placebo-based experiments, the Commission could not confirm the existence of this fluid and convincingly demonstrated that the positive effects attributed to Mesmer's techniques were the result of suggestion and imagination.
Franklin's numerous other inventions include bifocal glasses[5], the glass armonica, the flexible catheter, the odometer, and swimming fins. Franklin was also the first to suggest daylight savings time.
On his many ocean trips he carefully monitored temperatures and currents, thereby discovering the Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean.
Politician
In 1751, after serving as a clerk 15 years, Franklin was elected to the Pennsylvania Assembly. He used his new position to advance civic projects such as pushing legislation to maintain and light the streets. One of the primary issues faced by the Assembly was keeping their frontier border safe from Indian attacks orchestrated by the French. There was frequent conflict between the Assembly and the Proprietary leadership of the Penn family. The Penns controlled a vast majority of the lands in Pennsylvania, however, forbid them to be taxed which hampered the Assembly's ability to build an adequate militia. In 1753, Franklin was promoted to the position of Deputy Postmaster for the Colonies, which he would share with William Hunter, by the British government. The industrious Franklin, who frequently took inspection tours throughout the colonies, revamped the postal system to be more efficient, speeding up delivery times and creating the home delivery system. From visiting the colonies first hand, coupled with the increasing need for frontier defense, led Franklin to believe that some form of unification of the colonies was necessary. In June 1754, a conference was called by the London Board of Trade to meet in Albany, New York to discuss a more unified defense. Franklin presented his Albany Plan of Union, which called for a "General Government" that dealt solely with defense and left all other legislation to the colonies. The Plan was approved by the conference but was unanimously rejected by the colonial assemblies.
Mission to London
In January of 1757, demonstrating its frustration with the Proprietors, the Assembly elected to send Franklin to London. Franklin attempted to argue that the colonists should be afforded the same rights as other British citizens, with the ability to govern and tax through an elected legislature. His attempts to persuade this to both Thomas Penn and Parliament failed. Although his mission was over by 1758, Franklin lingered in London for another four years. He enjoyed his time meeting with the local intellectuals and political radicals, and with a touch of regret returned to Philadelphia in 1762. His return to Philadelphia was to be short-lived. In the 1764 elections, Franklin failed to be reelected after a vicious pamphlet war labeled him as anti-German and Scottish, which made up a majority of Pennsylvania's frontier population. He found this to be a blessing in disguise when the Assembly elected to send him back to London to serve as their agent once again.
Stamp Act
Shortly after his arrival, the Parliament passed the Stamp Act of 1765, which ended up being a public relations nightmare for Franklin. Franklin had recommended a friend of his as collection officer for Pennsylvania, while Thomas Penn wisely stayed out of it. The Act was immensely unpopular in the colonies and Franklin's recommendation did little to garner him any respect. He sent a letter to Philadelphia that was made public urging the colonies to simply make the best of it, leading to the misconception that Franklin had something to do with authoring the Act. His reputation damaged, Franklin enlisted prominent London Quakers to write on his behalf, and he began his own writing campaign in the London press denouncing the Stamp Act. On February 13, 1766 sat before Parliament and argued his case against the Act, which led to its repeal. This fully restored his reputation in America and he was asked by the colonies of Georgia, Massachusetts, and New Jersey to serve as their agent as well. In June 1767, Parliament passed another tax on colonial goods called the Townshend Act. Franklin, still loyal to the crown, took a moderate approach - simultaneously denouncing the growing radicalism in the colonies while ridiculing the British government for imposing taxes without adequate representation. Most of Franklin's moderation in these issues can be attributed to the fact that he desired a government appointment to oversee colonial affairs. When he was not chosen, he began an essay writing campaign that aggressively attacked the Townshend Act.
Hutchinson letters
In 1773, Franklin came into possession of several letters written by Massachusetts governor Thomas Hutchinson to the British government. The letters urged Parliament to send troops to put down the growing rebellion in Boston. Franklin sent the letters to friends in the colony, who in turn publicly published them against his wishes. His intent was to pin the blame on people like Hutchinson for encouraging the unpopular policies, which he hoped would promote a spirit of reconciliation with Britain. He misjudged the situation, however, which led to the Massachusetts Assembly demanding that Parliament remove Hutchinson from his governorship. Franklin later admitted he had leaked the letters. He was interrogated in highly humiliating fashion before Parliament on January 29, 1775. He was stripped of his position of postmaster and returned to Philadelphia on May 5, 1775.
Continental Congress
Upon his return, Franklin was elected to the Second Continental Congress. On July 21, he presented plans for the Articles of Confederation, similar to his Albany Plan, which called for a strong central government and a congress with proportional representation. Most of his ideas were not included in the version Congress adopted in 1777. As popular sentiment for independence grew in early 1776, Franklin, along with Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, Roger Sherman, and Robert Livingston, was selected by Congress to draft the U.S. Declaration of Independence. The document was written primarily by Jefferson, with Franklin offering his editorial commentary. With America formally declaring it's sovereignty and the war going poorly, in December of 1776 Franklin was sent to France, along with Silas Deane and Arthur Lee, to secure aid for the rebellion.
Minister to France
Franklin arrived to great fanfare in France. Already popular for his lightning experiment, his flirtatious manner and wit made him a favorite among the courtiers. Franklin also proved himself to be a crafty diplomat. By the end of 1777, after the American victory at Saratoga, the French favored an alliance with the Americans which was dismissed by their ally Spain. Franklin played on the traditional hatred between the British and the French, using the press to get his messages across. On February 5, 1778 America officially signed a treaty of alliance with France with the stipulation that they must have France's approval to negotiate peace with England. French aid proved to be critical to the Americans success, most notably in October 1781 at Yorktown in which the support of French naval forces and ground troops caused the British to surrender. This gave America the leverage it needed to negotiate peace with England and Franklin, along with John Jay and John Adams, negotiated the Treaty of Paris.
Constitutional Convention
Franklin arrived back in Philadelphia in September 1785. The Articles of Confederation, which were ratified by all the colonies in 1781, proved to be inefficient for governing the new nation, particularly because they granted the national government no power to levy taxes. In 1787 the Constitutional Convention convened in Philadelphia to write a new Constitution and Franklin, at the age of 81, was the oldest delegate. Franklin's role was largely honorific and his major contribution was his calming influence in the heated debate over representation.
Slavery
Franklin's final political activism dealt with the issue of slavery. Franklin, who himself had been a slave owner[6], joined the Pennsylvania Abolition Society and became their president in 1787. The Society had hoped he would bring up the issue of slavery at the Constitutional Convention, which he declined to do, realizing that it would be too contentious of an issue. In November 1789, he published his Address to the Public which appealed for the emancipation of slaves and the further education of free blacks.
Death
Franklin passed away in his bed on April 17, 1790 at the age of 84. He was buried with his wife at Christ Church in Philadelphia. Civic-minded to the end, Franklin's will established a 200 year trust fund for Boston and Philadelphia which was to be used to train and educate young craftsmen. Both cities have held true to Franklin's wishes, providing aid to students and establishing the Franklin Institute of Boston.
Further reading
See the longer guide under the Bibliography tab.
- Becker, Carl Lotus. "Benjamin Franklin," Dictionary of American Biography (1931) - vol 3, with hot links online
- Brands, Henry. The First American: The Life and Times of Benjamin Franklin (2000)- excellent long scholarly biography excerpt and text search
- Isaacson, Walter. Benjamin Franklin: An American Life (2004) - good recent biography excerpt and text search
- Ketcham, Ralph. Benjamin Franklin (1966) 228 pponline edition
- Morgan, Edmund S. Benjamn Franklin (2003) the best short introduction excerpt and text search
- Van Doren, Carl. Benjamin Franklin (1938), standard older biography excerpt and text search
- Wright, Esmond. Franklin of Philadelphia (1986) - excellent scholarly study excerpt and text search
Notes
- ↑ Although there were reports of his death, nothing was confirmed.
- ↑ While Franklin claimed that William was illegitimate, there is speculation among historians that Deborah was his mother.
- ↑ The charge is contained in a layer of the conductor facing the glass and the glass (the dielectricum) increases the capacitance of the jar (amount of charge that can be held).
- ↑ Theater of Electricity Exhibit, "Franklin's Kite" (Museum of Science, Boston; last accessed March 6, 2009); How Did Benjamin Franklin's Kite Experiment Work?. Retrieved on 03-06-2009.
- ↑ Benjamin Franklin - Father of the Bifocal. Retrieved on 03-06-2009.
- ↑ Franklin owned two slaves, which he eventually freed, and also ran advertisements for slave sales in his Pennsylvania Gazette.